Stabilization of Fo/Vo/Ao by a radial electric field
- PMID: 27857597
- PMCID: PMC5036770
- DOI: 10.2142/biophysics.7.99
Stabilization of Fo/Vo/Ao by a radial electric field
Abstract
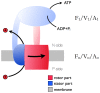
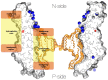
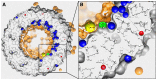
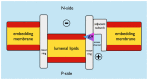
The membrane domain of rotary ATPases (Fo/Vo/Ao) contains a membrane-embedded rotor ring which rotates against an adjacent cation channel-forming subunit during catalysis. The mechanism that allows stabilization of the highly mobile and yet tightly connected domains during operation while not impeding rotation is unknown. Remarkably, all known ATPase rotor rings are filled by lipids. In the crystal structure of the rotor ring of a V-ATPase from Enterococcus hirae the ring filling lipids form a proper membrane that is lower with respect to the embedding membrane surrounding both subunits. I propose first, that a vertical shift between lumenal lipids and embedding outside membrane is a general feature of rotor rings and second that it leads to a radial potential fall-off between rotor ring and cation channel, creating attractive forces that impact rotor-stator interaction in Fo/Vo/Ao during rotation.
Keywords: ATP synthase; electrochemical gradient; membrane protein; transmembrane electric field.
Figures
References
-
- Boyer P. The ATP synthase-a splendid molecular machine. Annu Rev Biochem. 1997;66:717–49. - PubMed
-
- Wilkens S. Rotary molecular motors. Adv Protein Chem. 2005;71:345–82. - PubMed
-
- Junge W, Sielaff H, Engelbrecht S. Torque generation and elastic power transmission in the rotary F(o)F(1)-ATPase. Nature. 2009;459:364–70. - PubMed
-
- Noji H, Yasuda R, Yoshida M, Kinosita K. Direct observation of the rotation of F1-ATPase. Nature. 1997;386:299–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
