A bifunctional aminoglycoside acetyltransferase/phosphotransferase conferring tobramycin resistance provides an efficient selectable marker for plastid transformation
- PMID: 27858324
- PMCID: PMC5306187
- DOI: 10.1007/s11103-016-0560-x
A bifunctional aminoglycoside acetyltransferase/phosphotransferase conferring tobramycin resistance provides an efficient selectable marker for plastid transformation
Abstract
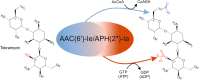
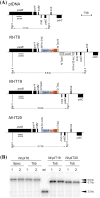
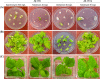
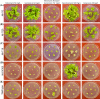
A new selectable marker gene for stable transformation of the plastid genome was developed that is similarly efficient as the aadA, and produces no background of spontaneous resistance mutants. More than 25 years after its development for Chlamydomonas and tobacco, the transformation of the chloroplast genome still represents a challenging technology that is available only in a handful of species. The vast majority of chloroplast transformation experiments conducted thus far have relied on a single selectable marker gene, the spectinomycin resistance gene aadA. Although a few alternative markers have been reported, the aadA has remained unrivalled in efficiency and is, therefore, nearly exclusively used. The development of new marker genes for plastid transformation is of crucial importance to all efforts towards extending the species range of the technology as well as to those applications in basic research, biotechnology and synthetic biology that involve the multistep engineering of plastid genomes. Here, we have tested a bifunctional resistance gene for its suitability as a selectable marker for chloroplast transformation. The bacterial enzyme aminoglycoside acetyltransferase(6')-Ie/aminoglycoside phosphotransferase(2″)-Ia possesses an N-terminal acetyltransferase domain and a C-terminal phosphotransferase domain that can act synergistically and detoxify aminoglycoside antibiotics highly efficiently. We report that, in combination with selection for resistance to the aminoglycoside tobramycin, the aac(6')-Ie/aph(2″)-Ia gene represents an efficient marker for plastid transformation in that it produces similar numbers of transplastomic lines as the spectinomycin resistance gene aadA. Importantly, no spontaneous antibiotic resistance mutants appear under tobramycin selection.
Keywords: Bifunctional enzyme; Nicotiana tabacum; Plastid transformation; Selectable marker; Tobramycin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transformation of the Plastid Genome in Tobacco: The Model System for Chloroplast Genome Engineering.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2317:135-153. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1472-3_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34028766
-
Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase as selectable marker for plastid transformation.Plant Mol Biol. 2011 Jul;76(3-5):443-51. doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9678-4. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Plant Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20721602
-
Efficient plastid transformation in tobacco using the aphA-6 gene and kanamycin selection.Mol Genet Genomics. 2002 Sep;268(1):19-27. doi: 10.1007/s00438-002-0738-6. Epub 2002 Aug 21. Mol Genet Genomics. 2002. PMID: 12242495
-
The chloroplast transformation toolbox: selectable markers and marker removal.Plant Biotechnol J. 2011 Jun;9(5):540-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00604.x. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Plant Biotechnol J. 2011. PMID: 21426476 Review.
-
Advances of selectable marker genes in plastid genetic engineering.Yi Chuan. 2017 Sep 20;39(9):810-827. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.16-433. Yi Chuan. 2017. PMID: 28936979 Review.
Cited by
-
N-acetyltransferase AAC(3)-I confers gentamicin resistance to Phytophthora palmivora and Phytophthora infestans.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Nov 27;19(1):265. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1642-0. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31775609 Free PMC article.
-
Marker-Free Transplastomic Plants by Excision of Plastid Marker Genes Using Directly Repeated DNA Sequences.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2317:95-107. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1472-3_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34028764
-
Selectable Markers and Reporter Genes for Engineering the Chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Biology (Basel). 2018 Oct 10;7(4):46. doi: 10.3390/biology7040046. Biology (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30309004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small serine recombination systems ParA-MRS and CinH-RS2 perform precise excision of plastid DNA.Plant Biotechnol J. 2017 Dec;15(12):1577-1589. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12740. Epub 2017 May 16. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 28421718 Free PMC article.
-
Phytodetoxification of TNT by transplastomic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) expressing a bacterial nitroreductase.Plant Mol Biol. 2017 Sep;95(1-2):99-109. doi: 10.1007/s11103-017-0639-z. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Plant Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28762129
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

