Fixator-assisted tibial lengthening over a plate in a patient with sequelae of poliomyelitis
- PMID: 27858886
- PMCID: PMC5591134
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005252
Fixator-assisted tibial lengthening over a plate in a patient with sequelae of poliomyelitis
Abstract
There are many techniques for limb lengthening. Lengthening over a plate is an alternative choice of fixation in children or when nailing is difficult. We present a new technique for tibial lengthening with using a monolateral external fixator over a lengthening plate.Lengthening over an intramedullary nail is a commonly used method in patients with short stature or limb-length discrepancy. However, in patients with a narrow and excessively sclerotic intramedullary cavity in the pediatric age group where the skeletal system has not yet fully developed, difficulties have been observed in lengthening methods with nailing.Therefore, in these cases, the use of lengthening techniques over a plate is an alternative treatment option. Nevertheless, in lengthening techniques over a plate, if one side of the osteotomy area cannot be fixed, associated mechanical axis problems have been reported.We applied tibia lengthening with external fixator assistance over a custom-made lengthening plate in a patient with sequelae of poliomyelitis. This new lengthening technique applied over a plate could be the solution to the problems observed in other lengthening techniques over a plate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




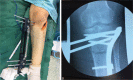
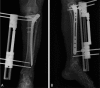

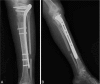

References
-
- Simpson AH, Cole AS, Kenwright J. Leg lengthening over an intramedullary nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1999; 81:1041–1045. - PubMed
-
- Ilizarov GA. Clinical application of the tension-stress effect for limb lengthening. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1990; 250:8–26. - PubMed
-
- Paley D. Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1990; 250:81–104. - PubMed
-
- Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Paremain G, et al. Femoral lengthening over an intramedullary nail: a matched-case comparison with Ilizarov femoral lengthening. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1997; 79:1464–1480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

