Protein Surface Mimetics: Understanding How Ruthenium Tris(Bipyridines) Interact with Proteins
- PMID: 27860106
- PMCID: PMC5347857
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201600552
Protein Surface Mimetics: Understanding How Ruthenium Tris(Bipyridines) Interact with Proteins
Abstract
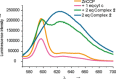
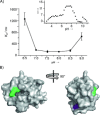
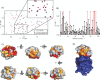
Protein surface mimetics achieve high-affinity binding by exploiting a scaffold to project binding groups over a large area of solvent-exposed protein surface to make multiple cooperative noncovalent interactions. Such recognition is a prerequisite for competitive/orthosteric inhibition of protein-protein interactions (PPIs). This paper describes biophysical and structural studies on ruthenium(II) tris(bipyridine) surface mimetics that recognize cytochrome (cyt) c and inhibit the cyt c/cyt c peroxidase (CCP) PPI. Binding is electrostatically driven, with enhanced affinity achieved through enthalpic contributions thought to arise from the ability of the surface mimetics to make a greater number of noncovalent interactions than CCP with surface-exposed basic residues on cyt c. High-field natural abundance 1 H,15 N HSQC NMR experiments are consistent with surface mimetics binding to cyt c in similar manner to CCP. This provides a framework for understanding recognition of proteins by supramolecular receptors and informing the design of ligands superior to the protein partners upon which they are inspired.
Keywords: molecular recognition; protein surface recognition; protein-protein interactions; receptors; supramolecular chemistry.
© 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

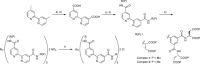

References
-
- Arkin M. R., Wells J. A., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2004, 3, 301–317. - PubMed
-
- Wilson A. J., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3289–3300. - PubMed
-
- Edfeldt F. N. B., Folmer R. H. A., Breeze A. L., Drug Discovery Today 2011, 16, 284–287. - PubMed
-
- Waring M. J., Arrowsmith J., Leach A. R., Leeson P. D., Mandrell S., Owen R. M., Pairaudeau G., Pennie W. D., Pickett S. D., Wang J., Wallace O., Weir A., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2015, 14, 475–486. - PubMed
-
- Azzarito V., Long K., Murphy N. S., Wilson A. J., Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 161–173. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

