A functionally conserved Zn2 Cys6 binuclear cluster transcription factor class regulates necrotrophic effector gene expression and host-specific virulence of two major Pleosporales fungal pathogens of wheat
- PMID: 27860150
- PMCID: PMC6638278
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12511
A functionally conserved Zn2 Cys6 binuclear cluster transcription factor class regulates necrotrophic effector gene expression and host-specific virulence of two major Pleosporales fungal pathogens of wheat
Abstract
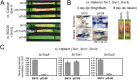
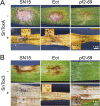
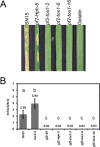
The fungus Parastagonospora nodorum is the causal agent of Septoria nodorum blotch of wheat (Triticum aestivum). The interaction is mediated by multiple fungal necrotrophic effector-dominant host sensitivity gene interactions. The three best-characterized effector-sensitivity gene systems are SnToxA-Tsn1, SnTox1-Snn1 and SnTox3-Snn3. These effector genes are highly expressed during early infection, but expression decreases as the infection progresses to tissue necrosis and sporulation. However, the mechanism of regulation is unknown. We have identified and functionally characterized a gene, referred to as PnPf2, which encodes a putative zinc finger transcription factor. PnPf2 deletion resulted in the down-regulation of SnToxA and SnTox3 expression. Virulence on Tsn1 and Snn3 wheat cultivars was strongly reduced. The SnTox1-Snn1 interaction remained unaffected. Furthermore, we have also identified and deleted an orthologous PtrPf2 from the tan spot fungus Pyrenophora tritici-repentis which possesses a near-identical ToxA that was acquired from P. nodorum via horizontal gene transfer. PtrPf2 deletion also resulted in the down-regulation of PtrToxA expression and a near-complete loss of virulence on Tsn1 wheat. We have demonstrated, for the first time, evidence for a functionally conserved signalling component that plays a role in the regulation of a common/horizontally transferred effector found in two major fungal pathogens of wheat.
Keywords: Parastagonospora nodorum; Pyrenophora tritici-repentis; Septoria nodorum blotch; SnTox3; ToxA; effector regulation; tan spot.
© 2016 THE AUTHORS. MOLECULAR PLANT PATHOLOGY PUBLISHED BY BRITISH SOCIETY FOR PLANT PATHOLOGY AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
Figures


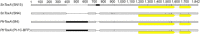

Similar articles
-
Differential effector gene expression underpins epistasis in a plant fungal disease.Plant J. 2016 Aug;87(4):343-54. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13203. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Plant J. 2016. PMID: 27133896 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of Variable Disease Expression Conferred by Inverse Gene-For-Gene Interactions in the Wheat-Parastagonospora nodorum Pathosystem.Plant Physiol. 2019 May;180(1):420-434. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00149. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30858234 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the Roles of Host Gene-Necrotrophic Effector Interactions in Governing Susceptibility of Durum Wheat to Tan Spot and Septoria nodorum Blotch.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Dec 7;6(12):4139-4150. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.036525. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 27777262 Free PMC article.
-
The Necrotrophic Pathogen Parastagonospora nodorum Is a Master Manipulator of Wheat Defense.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2023 Dec;36(12):764-773. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-05-23-0067-IRW. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2023. PMID: 37581456 Review.
-
Biology and molecular interactions of Parastagonospora nodorum blotch of wheat.Planta. 2021 Dec 16;255(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03796-w. Planta. 2021. PMID: 34914013 Review.
Cited by
-
Endophytic fungi from kale (Brassica oleracea var. acephala) modify roots-glucosinolate profile and promote plant growth in cultivated Brassica species. First description of Pyrenophora gallaeciana.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 5;13:981507. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.981507. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36274741 Free PMC article.
-
Maize responsiveness to Azospirillum brasilense: Insights into genetic control, heterosis and genomic prediction.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 7;14(6):e0217571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217571. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31173600 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor Repertoire of Necrotrophic Fungal Phytopathogen Ascochyta rabiei: Predominance of MYB Transcription Factors As Potential Regulators of Secretome.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jun 14;8:1037. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01037. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28659964 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Interactions between Wheat and Wheat Pathogens: Zymoseptoria tritici, Fusarium spp. and Parastagonospora nodorum.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 10;19(4):1138. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041138. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29642627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of nuclear processes in fungal plant pathogens.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Aug 3;19(8):e1011525. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011525. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37535497 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benedikz, P.W. , Mappledoram, C.J. and Scott, P.R. (1981) A laboratory technique for screening cereals for resistance to Septoria nodorum using detached seedling leaves. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 77, 667–668.
-
- Cho, Y. , Ohm, R.A. , Grigoriev, I.V. and Srivastava, A. (2013) Fungal‐specific transcription factor AbPf2 activates pathogenicity in Alternaria brassicicola . Plant J. 75, 498–514. - PubMed
-
- Ciuffetti, L.M. , Manning, V.A. , Pandelova, I. , Betts, M.F. and Martinez, J.P. (2010) Host‐selective toxins, Ptr ToxA and Ptr ToxB, as necrotrophic effectors in the Pyrenophora tritici‐repentis–wheat interaction. New Phytol. 187, 911–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

