Neutrophil and Monocyte Function in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Undergoing Antiviral Therapy with Regimens Containing Protease Inhibitors with and without Interferon
- PMID: 27861593
- PMCID: PMC5115763
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166631
Neutrophil and Monocyte Function in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Undergoing Antiviral Therapy with Regimens Containing Protease Inhibitors with and without Interferon
Erratum in
-
Correction: Neutrophil and Monocyte Function in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Undergoing Antiviral Therapy with Regimens Containing Protease Inhibitors with and without Interferon.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 20;12(1):e0170913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170913. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28107531 Free PMC article.
Abstract
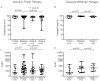
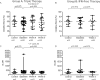
Real-life data showed an increased incidence of bacterial infections in patients with advanced liver disease receiving a protease inhibitor (PI)-containing antiviral regimen against hepatitis C (HCV). However, the causes of this event are unknown. We hypothesized that PIs might impair innate immune responses through the inhibition of proteases participating in the anti-bacterial functions of neutrophils and monocytes. The aims of the study were to assess phagocytic and oxidative burst capacity in neutrophils and monocytes obtained from patients receiving a PI containing-antiviral regimen, and to determine cytokine secretion after neutrophil stimulation with flagellin. Forty patients with chronic HCV (80% with cirrhosis) were enrolled in the study, 28 received triple therapy (Group A) with pegylated-interferon and ribavirin for 4 weeks followed by the addition of a PI (telaprevir, boceprevir or simeprevir), and 12 patients received an interferon-free regimen (Group B) with simeprevir and sofosbuvir. Phagocytosis and oxidative burst capacity were analyzed by flow cytometry at baseline, week 4, and week 8 of therapy. In neutrophils from Group A patients, oxidative burst rate and oxidative enzymatic activity per cell significantly decreased throughout the study period (p = 0.014 and p = 0.010, respectively). Pairwise comparisons showed a decrease between baseline and week 4 and 8 of therapy. No differences were observed after the introduction of the PI. The oxidative enzymatic activity per cell in monocytes significantly decrease during the study period (p = 0.042) due to a decrease from baseline to week 8 of therapy (p = 0.037) in patients from Group A. None of these findings were observed in Group B patients. Cytokine secretion did not significantly change during the study in both groups. In conclusion, our data suggest that the use interferon (rather than the PI) has a deleterious effect on neutrophil and monocyte phagocytic and oxidative burst capacity in this cohort of patients with HCV-related advanced liver fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
MCL has received advisory fees from Janssen, BMS and Gilead. SL has received advisory fees from Janssen, Gilead and Abbvie. ZM has received advisory fees from BMS. XF has received advisory fees from Gilead, Abbvie and Janssen. The other authors have declared no competing interest. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The combination of simeprevir and sofosbuvir is more effective than that of peginterferon, ribavirin, and sofosbuvir for patients with hepatitis C-related Child's class A cirrhosis.Gastroenterology. 2015 Apr;148(4):762-70.e2; quiz e11-2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.12.027. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 25557952 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment with PEG-interferon and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C increases neutrophil and monocyte chemotaxis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Sep;1173:847-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04623.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19758237 Clinical Trial.
-
Hepatitis C virus NS3 protease genotyping and drug concentration determination during triple therapy with telaprevir or boceprevir for chronic infection with genotype 1 viruses, southeastern France.J Med Virol. 2014 Nov;86(11):1868-76. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24016. Epub 2014 Jul 23. J Med Virol. 2014. PMID: 25052594
-
[Hepatitis C: diagnosis, anti-viral therapy, after-care. Hungarian consensus guideline].Orv Hetil. 2015 Mar 1;156(9):343-51. doi: 10.1556/OH.2015.30106. Orv Hetil. 2015. PMID: 25702254 Review. Hungarian.
-
Phase III results of Boceprevir in treatment naïve patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1.Liver Int. 2012 Feb;32 Suppl 1:27-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02725.x. Liver Int. 2012. PMID: 22212568 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic Changes of the Frequency of Classic and Inflammatory Monocytes Subsets and Natural Killer Cells in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients Treated by Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;2017:3612403. doi: 10.1155/2017/3612403. Epub 2017 May 8. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28567369 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid Cells during Viral Infections and Inflammation.Viruses. 2019 Feb 19;11(2):168. doi: 10.3390/v11020168. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30791481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correction: Neutrophil and Monocyte Function in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Undergoing Antiviral Therapy with Regimens Containing Protease Inhibitors with and without Interferon.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 20;12(1):e0170913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170913. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28107531 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

