A Real-World Multicentre Retrospective Study of Paclitaxel-Bevacizumab and Maintenance Therapy as First-Line for HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 27861874
- PMCID: PMC6220933
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25685
A Real-World Multicentre Retrospective Study of Paclitaxel-Bevacizumab and Maintenance Therapy as First-Line for HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
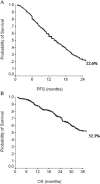
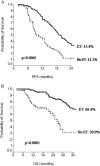
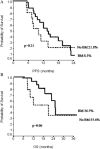
Bevacizumab in combination with taxanes in HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients has shown improved progression-free survival (PFS), despite the lack of clear overall survival (OS) benefit. We performed a retrospective analysis to evaluate the impact of paclitaxel-bevacizumab and of maintenance therapy with bevacizumab (BM) and endocrine therapy (ET) in the real-world practice. We identified 314 HER2-negative MBC patients treated in 12 cancer centers. Overall, the median PFS and OS were 14 and 40 months, respectively. Among the 254 patients potentially eligible for BM, 183 received BM after paclitaxel discontinuation until progression/toxicity. PFS and OS were improved in patients who had received BM in comparison with those potentially eligible but who did not receive BM (P< 0.0001 and P = 0.001, respectively). Results were confirmed when adjusting for propensity score. Among the 216 hormone-receptor positive patients eligible for BM, a more favorable PFS and OS were observed when maintenance ET was administered (P < 0.0001). Multivariate analysis showed that PS, BM, number of disease sites and maintenance ET were related to PFS, while response and maintenance ET were related to OS. In hormone-receptor positive patients, BM produced a significant PFS and a trend towards OS benefit only in absence of maintenance ET (P = 0.0007 and P = 0.06, respectively). In the triple-negative subgroup, we observed a trend towards a better OS for patients who received BM (P = 0.06), without differences in PFS (P = 0.21). Our results confirmed the efficacy of first-line paclitaxel-bevacizumab in real-world practice; both BM and maintenance ET significantly improved PFS and OS compared to no maintenance therapies. J. Cell. Physiol. 232: 1571-1578, 2017. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
First-line bevacizumab plus paclitaxel in Japanese patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer: subgroup results from the randomized Phase III MERiDiAN trial.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2017 May 1;47(5):385-392. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyx001. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28158579 Clinical Trial.
-
Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab or paclitaxel as first-line treatment for HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer in a multicenter national observational study.Ann Oncol. 2016 Sep;27(9):1725-32. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw260. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27436849
-
Cost-effectiveness of bevacizumab plus paclitaxel versus paclitaxel for the first-line treatment of HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer in specialist oncology centers in France.BMC Cancer. 2019 Feb 11;19(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5335-8. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30744578 Free PMC article.
-
Bevacizumab in combination with a taxane for the first-line treatment of HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2011 May;15 Suppl 1:1-12. doi: 10.3310/hta15suppl1/01. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21609648 Review.
-
Bevacizumab: a review of its use in combination with paclitaxel or capecitabine as first-line therapy for HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.Drugs. 2011 Nov 12;71(16):2213-29. doi: 10.2165/11207720-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 22035518 Review.
Cited by
-
Body mass index in HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer treated with first-line paclitaxel and bevacizumab.Cancer Biol Ther. 2018 Apr 3;19(4):328-334. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1416938. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29336662 Free PMC article.
-
Front-Line Bevacizumab plus Chemotherapy with or without Maintenance Therapy for Metastatic Breast Cancer: An Observational Study by the Hellenic Oncology Research Group.Curr Oncol. 2022 Feb 17;29(2):1237-1251. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29020105. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35200604 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term response to first-line bevacizumab-based therapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer: results of the observational "LORENA" study.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Sep 17;11:5845-5852. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S170303. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30271167 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Fulvestrant 500 mg in Endocrine Therapy-Naïve Postmenopausal Women with Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer in the UK.Pharmacoecon Open. 2019 Dec;3(4):559-570. doi: 10.1007/s41669-019-0134-3. Pharmacoecon Open. 2019. PMID: 31025302 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapeutic interventions of Triple Negative Breast Cancer.J Transl Med. 2018 May 30;16(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1514-7. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29848327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banerjee S, A'Hern R, Detre S, Littlewood‐Evans AJ, Evans DB, Dowsett M, Martin LA. 2010. Biological evidence for dual antiangiogenic‐antiaromatase activity of the VEGFR inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584 in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 16:4178–4187. - PubMed
-
- Bennouna J, Sastre J, Arnold D, Österlund P, Greil R, Van Cutsem E,, von Moos R, Viéitez JM, Bouché O, Borg C, Steffens CC, Alonso‐Orduña V, Schlichting C, Reyes‐Rivera I, Bendahmane B, André T, Kubicka S; ML18147 Study Investigators. 2013. Continuation of bevacizumab after first progression in metastatic colorectal cancer (ML18147): A randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14:29–37. - PubMed
-
- Bottini A, Generali D, Brizzi MP, Fox SB, Bersiga A, Bonardi S, Allevi G, Aguggini S, Bodini G, Milani M, Dionisio R, Bernardi C, Montruccoli A, Bruzzi P, Harris AL, Dogliotti L, Berruti A. 2006. Randomized phase II trial of letrozole and letrozole plus low‐dose metronomic oral cyclophosphamide as primary systemic treatment in elderly breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 24:3623–3628. - PubMed
-
- D'Agostino RB, Jr. 1998. Propensity score methods for bias reduction in the comparison of a treatment to a non‐randomized control group. Stat Med 17:2265–2281. - PubMed
-
- Delaloge S, Pérol D, Courtinard C, Brain E, Asselain B, Bachelot T, Debled M, Dieras V, Campone M, Levy C, Jacot W, Lorgis V, Veyret C, Dalenc F, Ferrero JM, Uwer L, Kerbrat P, Goncalves A, Mouret‐Reynier MA, Petit T, Jouannaud C, Van Lemmens L, Chenuc G, Guesmia T, Robain M, Cailliot C. 2016. Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab or paclitaxel as first‐line treatment for hER2‐negative metastatic breast cancer in a multicenter national observational study. Ann Oncol 27:1725–1732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

