Antiangiogenic Therapeutic Potential of Peptides Derived from the Molecular Motor KIF13B that Transports VEGFR2 to Plasmalemma in Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 27863212
- PMCID: PMC5225310
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.09.010
Antiangiogenic Therapeutic Potential of Peptides Derived from the Molecular Motor KIF13B that Transports VEGFR2 to Plasmalemma in Endothelial Cells
Erratum in
-
Correction.Am J Pathol. 2018 Aug;188(8):1934. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.06.002. Am J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 30033031 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
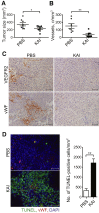
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) localized on the surface of endothelial cells (ECs) is a key determinant of the magnitude and duration of angiogenesis induced by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The kinesin family plus-end motor KIF13B transports VEGFR2 to the EC surface, and as such, specific inhibition of polarized VEGFR2 trafficking prevents angiogenesis. We designed a series of bioactive peptides based on deep analysis of VEGFR2-binding domain of KIF13B that compete specifically with VEGFR2 binding of KIF13B and thereby potently inhibit angiogenesis. Expression of these peptides by lentivirus prevents VEGF-induced capillary network formation in Matrigel plugs and neovascularization in vivo. A synthetic soluble, cell-permeable, 23-amino acid peptide termed kinesin-derived angiogenesis inhibitor (KAI) not only prevents interaction of VEGFR2 with KIF13B but also trafficking of VEGFR2 in the plus-end direction to the EC plasmalemma. Kinesin-derived angiogenesis inhibitor also inhibits VEGF-induced EC migration and tumor growth in human lung carcinoma xenografted in immunodeficient mice. Thus, we describe a novel class of peptides derived from the site of interaction of KIF13B with VEGFR2 that inhibit VEGFR2 trafficking and thereby starve cancer of blood supply.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
VEGFR2 Trafficking by KIF13B Is a Novel Therapeutic Target for Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Feb 1;62(2):5. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.2.5. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33533881 Free PMC article.
-
KIF13B-mediated VEGFR2 trafficking is essential for vascular leakage and metastasis in vivo.Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Oct 20;5(1):e202101170. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101170. Print 2022 Jan. Life Sci Alliance. 2021. PMID: 34670814 Free PMC article.
-
KIF13B regulates angiogenesis through Golgi to plasma membrane trafficking of VEGFR2.J Cell Sci. 2014 Oct 15;127(Pt 20):4518-30. doi: 10.1242/jcs.156109. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 25128562 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial SCUBE2 Interacts With VEGFR2 and Regulates VEGF-Induced Angiogenesis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Jan;37(1):144-155. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308546. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 27834687
-
From amino acid sequence to bioactivity: The biomedical potential of antitumor peptides.Protein Sci. 2016 Jun;25(6):1084-95. doi: 10.1002/pro.2927. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 27010507 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Teneurins: An Integrative Molecular, Functional, and Biomedical Overview of Their Role in Cancer.Front Neurosci. 2018 Dec 11;12:937. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00937. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30618566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular Delivery of Therapeutic Agents by Cell-Penetrating Peptides.Cells. 2023 Apr 1;12(7):1071. doi: 10.3390/cells12071071. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VEGFR2 Trafficking by KIF13B Is a Novel Therapeutic Target for Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Feb 1;62(2):5. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.2.5. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33533881 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Kinesins for Therapeutic Exploitation of Chromosomal Instability in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 18;17(4):685. doi: 10.3390/cancers17040685. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATF4 selectively regulates heat nociception and contributes to kinesin-mediated TRPM3 trafficking.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 3;12(1):1401. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21731-1. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33658516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shibuya M., Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:549–560. - PubMed
-
- Adams R.H., Alitalo K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:464–478. - PubMed
-
- Chung A.S., Ferrara N. Developmental and pathological angiogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:563–584. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:273–286. - PubMed
-
- Potente M., Gerhardt H., Carmeliet P. Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell. 2011;146:873–887. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

