Cancer cell CCL5 mediates bone marrow independent angiogenesis in breast cancer
- PMID: 27863423
- PMCID: PMC5356747
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13387
Cancer cell CCL5 mediates bone marrow independent angiogenesis in breast cancer
Abstract
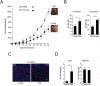
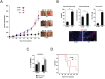
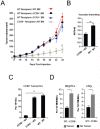
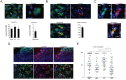
It has recently been suggested that the chemokine receptor (CCR5) is required for bone marrow (BM) derived endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) mediated angiogenesis. Here we show that suppression of either cancer cell produced CCL5, or host CCR5 leads to distinctive vascular and tumor growth defects in breast cancer. Surprisingly, CCR5 restoration in the BM alone was not sufficient to rescue the wild type phenotype, suggesting that impaired tumor growth associated with inhibiting CCL5/CCR5 is not due to defects in EPC biology. Instead, to promote angiogenesis cancer cell CCL5 may signal directly to endothelium in the tumor-stroma. In support of this hypothesis, we have also shown: (i) that endothelial cell CCR5 levels increases in response to tumor-conditioned media; (ii) that the amount of CCR5+ tumor vasculature correlates with invasive grade; and (iii) that inhibition of CCL5/CCR5 signaling impairs endothelial cell migration, associated with a decrease in activation of mTOR/AKT pathway members. Finally, we show that treatment with CCR5 antagonist results in less vasculature, impaired tumor growth, reduced metastases and improved survival. Taken as a whole, this work demonstrates that directly inhibiting CCR5 expressing vasculature constitutes a novel strategy for inhibiting angiogenesis and blocking metastatic progression in breast cancer.
Keywords: CCL5; CCR5; angiogenesis; breast cancer; shRNAi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors whose names are listed immediately above certify that they have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest, or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Folkman J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. 2002;29:15–8. - PubMed
-
- Gao D, Nolan DJ, Mellick AS, Bambino K, McDonnell K, Mittal V. EPCs control the angiogenic switch in mouse lung metastasis. Science. 2008;319:195–8. - PubMed
-
- Mellick AS, Plummer PN, Nolan DJ, Gao D, Bambino K, Hahn M, Catena R, Turner V, McDonnell K, Benezra R, Brink R, Swarbrick A, Mittal V. Using the transcription factor inhibitor of DNA binding 1 to selectively target endothelial progenitor cells offers novel strategies to inhibit tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Res. 2010;70:7273–82. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

