Immune-Mediated Protection and Pathogenesis of Chikungunya Virus
- PMID: 27864552
- PMCID: PMC5120763
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601426
Immune-Mediated Protection and Pathogenesis of Chikungunya Virus
Abstract
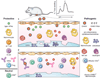
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is a re-emerging alphavirus that causes debilitating acute and chronic arthritis. Infection by CHIKV induces a robust immune response that is characterized by production of type I IFNs, recruitment of innate and adaptive immune cells, and development of neutralizing Abs. Despite this response, chronic arthritis can develop in some individuals, which may be due to a failure to eliminate viral RNA and Ag and/or persistent immune responses that cause chronic joint inflammation. In this review, based primarily on advances from recent studies in mice, we discuss the innate and adaptive immune factors that control CHIKV dissemination and clearance or contribute to pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Robinson MC. An epidemic of virus disease in Southern Province, Tanganyika Territory, in 1952–53. I. Clinical features. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 1955;49:28–32. - PubMed
-
- Staples JE, Breiman RF, Powers AM. Chikungunya fever: an epidemiological review of a re-emerging infectious disease. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2009;49:942–948. - PubMed
-
- PAHO/WHO. Chikungunya: PAHO/WHO Data, Maps and Statistics. 2016 http://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_topics&view=rdmore&cid=8379&..., ed.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

