Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with free vascularized fibular grafting: Results of 7.6-year follow-up
- PMID: 27865611
- PMCID: PMC6197408
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aott.2016.01.001
Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with free vascularized fibular grafting: Results of 7.6-year follow-up
Abstract
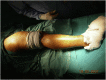
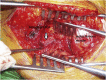
Objectives: The aim of this study was to determine long term follow up of the patients who had femoral head osteonecrosis and had been treated with free vascularized fibular grafting.
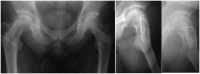
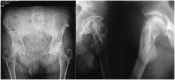
Patients and methods: We retrospectively reviewed 28 hips of 21 patients who had undergone free vascularized fibular grafting for the treatment of osteonecrosis of femoral head. There were 16 male and 5 female patients. The mean age of the patients at the time of surgery was 30.7 years (between 15 and 53 years). The mean follow-up time was 7.6 years (between 5 years and 9.2 years).
Results: During follow-up, one patient died because of leukemia, and one patient was lost. The remaining 26 hips of 19 patients were evaluated. According to the Ficat classification, at the time of surgery, 17 hips were in grade 2 and 9 hips were in grade 3. The post-operative Harris hip scores in grade II disease were excellent in 12 patients, good in 3 patients, and fair in 1 patient. In grade III disease, 1 patient was excellent, 5 patients were good, and 1 patient was fair. There was a significant increase in HHS scores (61 ± 9.7 vs 84 ± 17.8, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Free vascularized fibular grafting yields extremely good results, particularly in pre-collapse stages of disease in young patients. The operation time does not mark increased if the surgical team is "familiar" with the procedure, and the residual fibular defect of the donor site does not impair the functions of daily living.
Level of evidence: Level IV, Therapeutic study.
Keywords: Free vascularized fibular grafting; Osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
Copyright © 2016. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with free vascularized fibular grafting: results of 7.6-year follow-up.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016;50(3):323-9. doi: 10.3944/AOTT.2015.15.0328. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016. PMID: 27130389
-
Comparison of early results of vascularized and non-vascularized fibular grafting in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2011;45(5):326-34. doi: 10.3944/AOTT.2011.2259. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2011. PMID: 22032997
-
Free Vascularized Fibular Grafting Improves Vascularity Compared With Core Decompression in Femoral Head Osteonecrosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Sep;475(9):2230-2240. doi: 10.1007/s11999-017-5374-x. Epub 2017 May 4. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 28474152 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Revascularization of the femoral head in osteonecrosis.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1998 Jan-Feb;6(1):44-54. doi: 10.5435/00124635-199801000-00005. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1998. PMID: 9692940 Review.
-
[Therapeutic progress of avascular osteonecrosis of the femoral head using a fibular graft by vascular anastomosis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009 Jan;22(1):76-8. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009. PMID: 19203057 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
[Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with vascularized bone grafting].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Mar 15;35(3):381-386. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202006053. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33719249 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Effectiveness comparison between impacting bone graft and rotational osteotomy via surgical hip dislocation approach for avascular necrosis of femoral head at ARCO stage Ⅲ].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Apr 15;33(4):445-450. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201811120. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30983192 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Impacting bone graft via surgical hip dislocation approach versus core decompression and bone graft for avascular necrosis of femoral head at ARCO stage Ⅲ].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 May 15;33(5):531-536. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201901047. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31090343 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today?: A 5-Year Update.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020 Jun 17;102(12):1084-1099. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.19.01271. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020. PMID: 32282421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of sartorius muscle-pedicle and circumflex iliac deep bone flap grafts in the treatment of early non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head in young adults.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2019 Jul;53(4):255-259. doi: 10.1016/j.aott.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2019. PMID: 31031129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Urbaniak J.R., Coogan P.G., Gunneson E.B., Nunley J.A. Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with FVFG. A long-term follow-up study of one hundred and three hips. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1995;77:681–694. 1. - PubMed
-
- Scher M.A., Jakim I. Intertrochanteric osteotomy and autogenous bone-grafting for avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1993;75-A:1119–1133. - PubMed
-
- Zalavras C.G., Lieberman J.R. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014 Jul;22(7):455–464. - PubMed
-
- Sugioka Y. Transtrochanteric anterior rotational osteotomy of the femoral head in the treatment of osteonecrosis affecting the hip: a new osteotomy operation. Clin Orthop. 1978;130:191–201. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
