Sm-p80-Based Schistosomiasis Vaccine: Preparation for Human Clinical Trials
- PMID: 27865740
- PMCID: PMC5328854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2016.10.010
Sm-p80-Based Schistosomiasis Vaccine: Preparation for Human Clinical Trials
Abstract
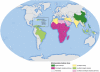
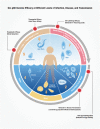
Mass antiparasitic drug administration programs and other control strategies have made important contributions in reducing the global prevalence of helminths. Schistosomiasis, however, continues to spread to new geographic areas. The advent of a viable vaccine and its deployment, coupled with existing control efforts, is expected to make significant headway towards sustained schistosomiasis control. In 2016, Science ranked the schistosomiasis vaccine as one of the top 10 vaccines that needs to be urgently developed. A vaccine that is effective against geographically distinct forms of intestinal/hepatic and urinary disease is essential to make a meaningful impact in global reduction of the disease burden. In this opinion article, we focus on salient features of schistosomiasis vaccines in different phases of the clinical development pipeline and highlight the Sm-p80-based vaccine which is now being prepared for human clinical trials.
Keywords: Schistosoma haematobium; Schistosoma japonicum; Schistosoma mansoni; neglected tropical disease (NTD); protective immunity; schistosomiasis; vaccine.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- El-Khoby T, Galal N, Fenwick A, et al. The epidemiology of schistosomiasis in Egypt: summary findings in nine governorates. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000 Feb;62(2 Suppl):88–99. - PubMed
-
- Hotez PJ, Molyneux DH, Fenwick A, et al. Control of neglected tropical diseases. N Engl J Med. 2007 Sep 6;357(10):1018–27. - PubMed
-
- Steinmann P, Keiser J, Bos R, Tanner M, Utzinger J. Schistosomiasis and water resources development: systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006 Jul;6(7):411–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

