Relationship Between Anemia and Mortality Outcomes in a National Acute Coronary Syndrome Cohort: Insights From the UK Myocardial Ischemia National Audit Project Registry
- PMID: 27866164
- PMCID: PMC5210321
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003348
Relationship Between Anemia and Mortality Outcomes in a National Acute Coronary Syndrome Cohort: Insights From the UK Myocardial Ischemia National Audit Project Registry
Abstract
Background: We aim to determine the prevalence of anemia in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients and compare their clinical characteristics, management, and clinical outcomes to those without anemia in an unselected national ACS cohort.
Methods and results: The Myocardial Ischemia National Audit Project (MINAP) registry collects data on all adults admitted to hospital trusts in England and Wales with diagnosis of an ACS. We conducted a retrospective cohort study by analyzing patients in this registry between January 2006 and December 2010 and followed them up until August 2011. Multiple logistic regressions were used to determine factors associated with anemia and the adjusted odds of 30-day mortality with 1 g/dL incremental hemoglobin increase and the 30-day and 1-year mortality for anemic compared to nonanemic groups. Analyses were adjusted for covariates. Our analysis of 422 855 patients with ACS showed that 27.7% of patients presenting with ACS are anemic and that these patients are older, have a greater prevalence of renal disease, peripheral vascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and previous acute myocardial infarction, and are less likely to receive evidence-based therapies shown to improve clinical outcomes. Finally, our analysis suggests that anemia is independently associated with 30-day (OR 1.28, 95% CI 1.22-1.35) and 1-year mortality (OR 1.31, 95% CI 1.27-1.35), and we observed a reverse J-shaped relationship between hemoglobin levels and mortality outcomes.
Conclusions: The prevalence of anemia in a contemporary national ACS cohort is clinically significant. Patients with anemia are older and multimorbid and less likely to receive evidence-based therapies shown to improve clinical outcomes, with the presence of anemia independently associated with mortality outcomes.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; anemia; mortality.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
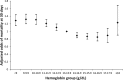
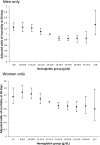
Comment in
-
Anemia and Acute Coronary Syndrome: Time for Intervention Studies.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Nov 19;5(11):e004908. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004908. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27866165 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aronson D, Suleiman M, Agmon Y, Suleiman A, Blich M, Kapeliovich M, Beyar R, Markiewicz W, Hammerman H. Changes in haemoglobin levels during hospital course and long‐term outcome after acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:1289–1296. - PubMed
-
- Giraldez RR, Sabatine MS, Morrow DA, Mohanavelu S, McCabe CH, Antman EM, Braunwald E. Baseline hemoglobin concentration and creatinine clearance composite laboratory index improves risk stratification in ST‐elevation myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 2009;157:517–524. - PubMed
-
- Al Falluji N, Lawrence‐Nelson J, Kostis JB, Lacy CR, Ranjan R, Wilson AC. Effect of anemia on 1‐year mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 2002;144:636–641. - PubMed
-
- Alexander KP, Chen AY, Wang TY, Rao SV, Newby LK, LaPointe NM, Ohman EM, Roe MT, Boden WE, Harrington RA, Peterson ED. Transfusion practice and outcomes in non‐ST‐segment elevation acute coronary syndromes. Am Heart J. 2008;155:1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Anker SD, Voors A, Okonko D, Clark AL, James MK, von Haehling S, Kjekshus J, Ponikowski P, Dickstein K. Prevalence, incidence, and prognostic value of anaemia in patients after an acute myocardial infarction: data from the OPTIMAAL trial. Eur Heart J. 2009;30:1331–1339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

