Deubiquitination and Stabilization of PD-L1 by CSN5
- PMID: 27866850
- PMCID: PMC5171205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.010
Deubiquitination and Stabilization of PD-L1 by CSN5
Abstract
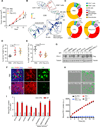
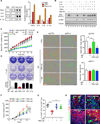
Pro-inflammatory cytokines produced in the tumor microenvironment lead to eradication of anti-tumor immunity and enhanced tumor cell survival. In the current study, we identified tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) as a major factor triggering cancer cell immunosuppression against T cell surveillance via stabilization of programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). We demonstrated that COP9 signalosome 5 (CSN5), induced by NF-κB p65, is required for TNF-α-mediated PD-L1 stabilization in cancer cells. CSN5 inhibits the ubiquitination and degradation of PD-L1. Inhibition of CSN5 by curcumin diminished cancer cell PD-L1 expression and sensitized cancer cells to anti-CTLA4 therapy.
Keywords: CSN5; PD-L1; TNF-α; anti-CTLA4; curcumin; deubiquitination.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Kumar A, Bharti AC. Anticancer potential of curcumin: preclinical and clinical studies. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:363–398. - PubMed
-
- Brahmer JR, Drake CG, Wollner I, Powderly JD, Picus J, Sharfman WH, Stankevich E, Pons A, Salay TM, McMiller TL, et al. Phase I study of single-agent anti-programmed death-1 (MDX-1106) in refractory solid tumors: safety, clinical activity, pharmacodynamics, and immunologic correlates. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010;28:3167–3175. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown JA, Dorfman DM, Ma FR, Sullivan EL, Munoz O, Wood CR, Greenfield EA, Freeman GJ. Blockade of programmed death-1 ligands on dendritic cells enhances T cell activation and cytokine production. J. Immunol. 2003;170:1257–1266. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

