Current applications and different approaches for microbial l-asparaginase production
- PMID: 27866936
- PMCID: PMC5156506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjm.2016.10.004
Current applications and different approaches for microbial l-asparaginase production
Abstract
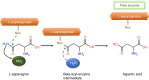
l-asparaginase (EC 3.5.1.1) is an enzyme that catalysis mainly the asparagine hydrolysis in l-aspartic acid and ammonium. This enzyme is presented in different organisms, such as microorganisms, vegetal, and some animals, including certain rodent's serum, but not unveiled in humans. It can be used as important chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of a variety of lymphoproliferative disorders and lymphomas (particularly acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and Hodgkin's lymphoma), and has been a pivotal agent in chemotherapy protocols from around 30 years. Also, other important application is in food industry, by using the properties of this enzyme to reduce acrylamide levels in commercial fried foods, maintaining their characteristics (color, flavor, texture, security, etc.) Actually, l-asparaginase catalyzes the hydrolysis of l-asparagine, not allowing the reaction of reducing sugars with this aminoacid for the generation of acrylamide. Currently, production of l-asparaginase is mainly based in biotechnological production by using some bacteria. However, industrial production also needs research work aiming to obtain better production yields, as well as novel process by applying different microorganisms to increase the range of applications of the produced enzyme. Within this context, this mini-review presents l-asparaginase applications, production by different microorganisms and some limitations, current investigations, as well as some challenges to be achieved for profitable industrial production.
Keywords: Acrylamide; Industrial production; Microbial production; Pharmaceutical application; l-asparaginase.
Copyright © 2016 Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Appel I.M., van Kessel-Bakvis C., Stigter R., Pieters R. Influence of two different regimens of concomitant treatment with asparaginase and dexamethasone on hemostasis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2007;21(11):2377–2380. - PubMed
-
- Mohan Kumar N.S., Shimray C.A., Indrani D., Manonmani H.K. Reduction of acrylamide formation in sweet bread with l-asparaginase treatment. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013;7(3):741–748.
-
- Medeiros Vinci R., Mestdagh F., De Meulenaer B. Acrylamide formation in fried potato products – present and future, a critical review on mitigation strategies. Food Chem. 2012;133(4):1138–1154.
-
- Keating M.J., Holmes R., Lerner S., Ho D.H. l-asparaginase and PEG asparaginase – past, present, and future. Leuk Lymphoma. 1993;10(suppl):153–157. - PubMed
-
- Narta U.K., Kanwar S.S., Azmi W. Pharmacological and clinical evaluation of l-asparaginase in the treatment of leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2007;61(3):208–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources