Two-Way Conversion between Lipogenic and Myogenic Fibroblastic Phenotypes Marks the Progression and Resolution of Lung Fibrosis
- PMID: 27867035
- PMCID: PMC5291816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.10.004
Two-Way Conversion between Lipogenic and Myogenic Fibroblastic Phenotypes Marks the Progression and Resolution of Lung Fibrosis
Erratum in
-
Two-Way Conversion between Lipogenic and Myogenic Fibroblastic Phenotypes Marks the Progression and Resolution of Lung Fibrosis.Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Apr 6;20(4):571. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.03.011. Cell Stem Cell. 2017. PMID: 28388434 No abstract available.
Abstract
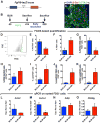
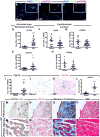
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a form of progressive interstitial lung disease with unknown etiology. Due to a lack of effective treatment, IPF is associated with a high mortality rate. The hallmark feature of this disease is the accumulation of activated myofibroblasts that excessively deposit extracellular matrix proteins, thus compromising lung architecture and function and hindering gas exchange. Here we investigated the origin of activated myofibroblasts and the molecular mechanisms governing fibrosis formation and resolution. Genetic engineering in mice enables the time-controlled labeling and monitoring of lipogenic or myogenic populations of lung fibroblasts during fibrosis formation and resolution. Our data demonstrate a lipogenic-to-myogenic switch in fibroblastic phenotype during fibrosis formation. Conversely, we observed a myogenic-to-lipogenic switch during fibrosis resolution. Analysis of human lung tissues and primary human lung fibroblasts indicates that this fate switching is involved in IPF pathogenesis, opening potential therapeutic avenues to treat patients.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
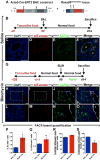
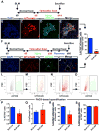
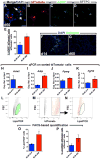
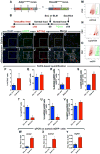

Comment in
-
Mesenchymal metamorphosis.Sci Transl Med. 2016 Dec 21;8(370):370ec202. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3700. Sci Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 28003541 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahlbrecht K, McGowan SE. In search of the elusive lipofibroblast in human lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014;307:L605–L608. - PubMed
-
- Asaki T, Konishi M, Miyake A, Kato S, Tomizawa M, Itoh N. Roles of fibroblast growth factor 10 (Fgf10) in adipogenesis in vivo. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2004;218:119–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

