Tracking sentence comprehension: Test-retest reliability in people with aphasia and unimpaired adults
- PMID: 27867260
- PMCID: PMC5113948
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroling.2016.06.001
Tracking sentence comprehension: Test-retest reliability in people with aphasia and unimpaired adults
Abstract
Purpose: Visual-world eyetracking is increasingly used to investigate online language processing in normal and language impaired listeners. Tracking changes in eye movements over time also may be useful for indexing language recovery in those with language impairments. Therefore, it is critical to determine the test-retest reliability of results obtained using this method.
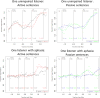
Methods: Unimpaired young adults and people with aphasia took part in two eyetracking sessions spaced about one week apart. In each session, participants completed a sentence-picture matching task in which they listened to active and passive sentences (e.g., The [N1+Auxwoman was] [Vvisiting/visited] [NP/PP2(by) the man]) and selected between two pictures with reversed thematic roles. We used intraclass correlations (ICCs) to examine the test-retest reliability of response measures (accuracy, reaction time (RT)) and online eye movements (i.e., the likelihood of fixating the target picture in each region of the sentence) in each participant group.
Results: In the unimpaired adults, accuracy was at ceiling (thus ICCs were not computed), with moderate ICCs for RT (i.e., 0.4 - 0.58) for passive sentences and low (<0.4) for actives. In individuals with aphasia, test-retest reliability was strong (0.59<ICC<0.75) for accuracy and excellent (>0.75) for RT for both sentence types. Similarly, for the unimpaired listeners, reliability of eye movements was moderate for passive sentences (NP/PP2 region) and low in all regions for active sentences. But, for the aphasic participant group, eye movement reliability was excellent for passive sentences (in the first second after sentence end) and strong for active sentences (V and NP/PP2 regions).
Conclusion: Results indicated moderate-to-low reliability for unimpaired listeners; however, reliable eye movement patterns were detected for processes specific to passive sentences (e.g., thematic reanalysis). In contrast, individuals with aphasia exhibited strong and stable performance across sentence types in response measures and online eye movements. These findings indicate that visual-world eyetracking provides a reliable measure of online sentence comprehension, and thus may be useful for investigating sentence processing changes over time.
Keywords: aphasia; eyetracking; sentence comprehension; test-retest reliability.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recovery of Online Sentence Processing in Aphasia: Eye Movement Changes Resulting From Treatment of Underlying Forms.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017 May 24;60(5):1299-1315. doi: 10.1044/2016_JSLHR-L-16-0108. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017. PMID: 28474086 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery of Sentence Production Processes Following Language Treatment in Aphasia: Evidence from Eyetracking.Front Hum Neurosci. 2017 Mar 13;11:101. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00101. eCollection 2017. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28348524 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking Passive Sentence Comprehension in Agrammatic Aphasia.J Neurolinguistics. 2012 Jan 1;25(1):31-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroling.2011.08.001. J Neurolinguistics. 2012. PMID: 22043134 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of sentence comprehension and production in aphasia: is there cross-modal generalisation?Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2018 Sep;28(6):937-965. doi: 10.1080/09602011.2016.1213176. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2018. PMID: 27610543 Review.
-
Sentence comprehension deficits in aphasia disorders: A systematic review of mapping therapy.Appl Neuropsychol Adult. 2024 Sep 8:1-9. doi: 10.1080/23279095.2024.2394091. Online ahead of print. Appl Neuropsychol Adult. 2024. PMID: 39244662 Review.
Cited by
-
Recovery of offline and online sentence processing in aphasia: Language and domain-general network neuroplasticity.Cortex. 2019 Nov;120:394-418. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2019.06.015. Epub 2019 Jul 13. Cortex. 2019. PMID: 31419597 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery of Online Sentence Processing in Aphasia: Eye Movement Changes Resulting From Treatment of Underlying Forms.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017 May 24;60(5):1299-1315. doi: 10.1044/2016_JSLHR-L-16-0108. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017. PMID: 28474086 Free PMC article.
-
Sentence comprehension test for Russian: A tool to assess syntactic competence.Front Psychol. 2023 Feb 10;14:1035961. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1035961. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36844341 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery of Sentence Production Processes Following Language Treatment in Aphasia: Evidence from Eyetracking.Front Hum Neurosci. 2017 Mar 13;11:101. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00101. eCollection 2017. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28348524 Free PMC article.
-
Online Eye Tracking for Aphasia: A Feasibility Study Comparing Web and Lab Tracking and Implications for Clinical Use.Brain Behav. 2024 Nov;14(11):e70112. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70112. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 39469815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastiaanse R, Edwards S. Word order and finiteness in Dutch and English Broca’s and Wernicke’s aphasia. Brain and Language. 2004;89(1):91–107. - PubMed
-
- Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software. 2015;67(1):1–48.
-
- Bennett CM, Miller MB. How reliable are the results from functional magnetic resonance imaging? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2010;1191:133–155. - PubMed
-
- Berndt RS, Mitchum CC, Haendiges AN. Comprehension of reversible sentences in “agrammatism”: a meta-analysis. Cognition. 1996;58(3):289–308. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
