Disorders of Transcriptional Regulation: An Emerging Category of Multiple Malformation Syndromes
- PMID: 27867341
- PMCID: PMC5109993
- DOI: 10.1159/000448747
Disorders of Transcriptional Regulation: An Emerging Category of Multiple Malformation Syndromes
Abstract
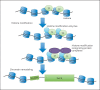
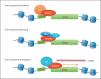
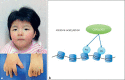
Some genetic disorders caused by mutations in genes encoding components of the transcriptional machinery as well as proteins involved in epigenetic modification of the genome share many overlapping features, such as facial dysmorphisms, growth problems and developmental delay/intellectual disability. As a basis for some shared phenotypic characteristics in these syndromes, a similar transcriptome disturbance, characterized by global transcriptional dysregulation, is believed to play a major role. In this review article, a general overview of gene transcription is provided, and the current knowledge of the mechanisms underlying some disorders of transcriptional regulation, such as Rubinstein- Taybi, Coffin-Siris, Cornelia de Lange, and CHOPS syndromes, are discussed.
Keywords: Chromatin remodeling; Malformation syndromes; Transcriptional regulation.
Figures



References
-
- Basel-Vanagaite L, Smirin-Yosef P, Essakow JL, Tzur S, Lagovsky I, et al. Homozygous MED25 mutation implicated in eye-intellectual disability syndrome. Hum Genet. 2015;134:577–587. - PubMed
-
- Castronovo P, Gervasini C, Cereda A, Masciadri M, Milani D, et al. Premature chromatid separation is not a useful diagnostic marker for Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Chromosome Res. 2009;17:763–771. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

