Force-plate analyses of balance following a balance exercise program during acute post-operative phase in individuals with total hip and knee arthroplasty: A randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 27867519
- PMCID: PMC5102164
- DOI: 10.1177/2050312116675097
Force-plate analyses of balance following a balance exercise program during acute post-operative phase in individuals with total hip and knee arthroplasty: A randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Objectives: Typical rehabilitation programs following total hip arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty include joint range of motion and muscle-strengthening exercises. Balance and balance exercises following total hip arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty have not received much attention. The purpose of this study was to determine whether an intervention of balance exercises added to a typical rehabilitation program positively affects patients' balance.
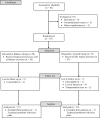
Methods: A total of 63 patients were provided with outpatient physical therapy at their home. Patients were randomly assigned to either typical (n = 33) or balance (n = 30) exercise group. The typical group completed seven typical surgery-specific joint range of motion and muscle-strengthening exercises, while the balance group completed the typical exercises plus three balance exercises. After 5 weeks of administering the rehabilitation program, patients' balance was assessed on a force plate using 95% ellipse area of the center of pressure amplitude.
Results: Patients in the balance group demonstrated significant reduction in the 95% ellipse area for the anterior and posterior lean standing conditions (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Balance exercises added to the typical outpatient physical therapy program resulted in significantly greater improvements in balance for participants with total hip arthroplasty or total knee arthroplasty, compared to the typical exercise program alone. Physical therapists might consider the use of balance exercises to improve balance in individuals in the acute post-operative phase following total hip arthroplasty or total knee arthroplasty.
Keywords: 95% ellipse area; Total hip arthroplasty; balance exercises; force plate; total knee arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of balance exercises in the acute post-operative phase following total hip and knee arthroplasty: A randomized clinical trial.SAGE Open Med. 2015 Feb 11;3:2050312115570769. doi: 10.1177/2050312115570769. eCollection 2015. SAGE Open Med. 2015. PMID: 26770765 Free PMC article.
-
Does the addition of hip strengthening exercises improve outcomes following total knee arthroplasty? A study protocol for a randomized trial.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016 Jun 13;17:259. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1104-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016. PMID: 27295978 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Incorporating hip abductor strengthening exercises into a rehabilitation program did not improve outcomes in people following total knee arthroplasty: a randomised trial.J Physiother. 2019 Jul;65(3):136-143. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 Jun 14. J Physiother. 2019. PMID: 31208916 Clinical Trial.
-
Guideline recommendations for post-acute postoperative physiotherapy in total hip and knee arthroplasty: are they used in daily clinical practice?Musculoskeletal Care. 2014 Sep;12(3):125-31. doi: 10.1002/msc.1067. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Musculoskeletal Care. 2014. PMID: 24497426 Review.
-
Hip Strengthening After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2024;12(6):373-379. doi: 10.22038/ABJS.2024.76202.3520. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2024. PMID: 38919739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Balance and proprioception impairment, assessment tools, and rehabilitation training in patients with total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Dec 20;22(1):1055. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04919-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34930190 Free PMC article.
-
Does total hip replacement impact on postural stability?BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019 May 17;20(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2598-9. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019. PMID: 31101048 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Balance Remains Impaired after Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Best Evidence Synthesis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 11;12(3):684. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030684. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Dynamic Balance Exercises Based on Visual Feedback on Physical Function, Balance Ability, and Depression in Women after Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 5;17(9):3203. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17093203. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32380679 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wegener L, Kisner C, Nichols D. Static and dynamic balance responses in persons with bilateral knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 1997; 25(1): 13–18. - PubMed
-
- Cross MJ, McCloskey DI. Position sense following surgical removal of joints in man. Brain Res 1973; 55(2): 443–445. - PubMed
-
- Barrack RL, Skinner HB, Cook SD, et al. Effect of articular disease and total knee arthroplasty on knee joint-position sense. J Neurophysiol 1983; 50(3): 684–687. - PubMed
-
- Karanjia PN, Ferguson JH. Passive joint position sense after total hip replacement surgery. Ann Neurol 1983; 13(6): 654–657. - PubMed
-
- Wada M, Kawahara H, Shimada S, et al. Joint proprioception before and after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002; 403(10): 161–167. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources