The HECT domain ubiquitin ligase HUWE1 targets unassembled soluble proteins for degradation
- PMID: 27867533
- PMCID: PMC5102030
- DOI: 10.1038/celldisc.2016.40
The HECT domain ubiquitin ligase HUWE1 targets unassembled soluble proteins for degradation
Abstract
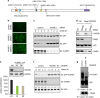
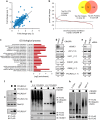
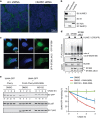
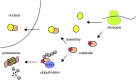
In eukaryotes, many proteins function in multi-subunit complexes that require proper assembly. To maintain complex stoichiometry, cells use the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation system to degrade unassembled membrane subunits, but how unassembled soluble proteins are eliminated is undefined. Here we show that degradation of unassembled soluble proteins (referred to as unassembled soluble protein degradation, USPD) requires the ubiquitin selective chaperone p97, its co-factor nuclear protein localization protein 4 (Npl4), and the proteasome. At the ubiquitin ligase level, the previously identified protein quality control ligase UBR1 (ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 1) and the related enzymes only process a subset of unassembled soluble proteins. We identify the homologous to the E6-AP carboxyl terminus (homologous to the E6-AP carboxyl terminus) domain-containing protein HUWE1 as a ubiquitin ligase for substrates bearing unshielded, hydrophobic segments. We used a stable isotope labeling with amino acids-based proteomic approach to identify endogenous HUWE1 substrates. Interestingly, many HUWE1 substrates form multi-protein complexes that function in the nucleus although HUWE1 itself is cytoplasmically localized. Inhibition of nuclear entry enhances HUWE1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation, suggesting that USPD occurs primarily in the cytoplasm. Altogether, these findings establish a new branch of the cytosolic protein quality control network, which removes surplus polypeptides to control protein homeostasis and nuclear complex assembly.
Keywords: HUWE1; p97/Cdc48; protein quality control (PQC); ubiquitin; unassembled soluble protein degradation (USPD).
Figures



Similar articles
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase HUWE1 acts through the N-Myc-DLL1-NOTCH1 signaling axis to suppress glioblastoma progression.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2022 Sep;42(9):868-886. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12334. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35848447 Free PMC article.
-
Solenoid architecture of HUWE1 contributes to ligase activity and substrate recognition.Mol Cell. 2021 Sep 2;81(17):3468-3480.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.06.032. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34314700 Free PMC article.
-
CRL4BRBBP7 targets HUWE1 for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jun 22;501(2):440-447. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.008. Epub 2018 May 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29738775
-
Ubiquitination by HUWE1 in tumorigenesis and beyond.J Biomed Sci. 2018 Sep 4;25(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0470-0. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 30176860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of the HUWE1 ubiquitin ligase in nervous system development, function and disease.Neural Dev. 2020 Apr 26;15(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13064-020-00143-9. Neural Dev. 2020. PMID: 32336296 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deubiquitinases USP20/33 promote the biogenesis of tail-anchored membrane proteins.J Cell Biol. 2021 May 3;220(5):e202004086. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202004086. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33792613 Free PMC article.
-
A Key Role for the Ubiquitin Ligase UBR4 in Myofiber Hypertrophy in Drosophila and Mice.Cell Rep. 2019 Jul 30;28(5):1268-1281.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.06.094. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31365869 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic profiling of VCP substrates links VCP to K6-linked ubiquitylation and c-Myc function.EMBO Rep. 2018 Apr;19(4):e44754. doi: 10.15252/embr.201744754. Epub 2018 Feb 21. EMBO Rep. 2018. PMID: 29467282 Free PMC article.
-
HUWE1 controls tristetraprolin proteasomal degradation by regulating its phosphorylation.Elife. 2023 Mar 24;12:e83159. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83159. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36961408 Free PMC article.
-
Convergence of orphan quality control pathways at a ubiquitin chain-elongating ligase.Mol Cell. 2025 Feb 20;85(4):815-828.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2025.01.002. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Mol Cell. 2025. PMID: 39879985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hegde RS, Lingappa VR. Membrane protein biogenesis: regulated complexity at the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 1997; 91: 575–582. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

