The Role of TLR4 on B Cell Activation and Anti- β2GPI Antibody Production in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome
- PMID: 27868072
- PMCID: PMC5102736
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/1719720
The Role of TLR4 on B Cell Activation and Anti- β2GPI Antibody Production in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Abstract
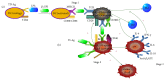
High titer of anti-β2-glycoprotein I antibodies (anti-β2GPI Ab) plays a pathogenic role in antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). Numerous studies have focused on the pathological mechanism in APS; however, little attention is paid to the immune mechanism of production of anti-β2GPI antibodies in APS. Our previous study demonstrated that Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) plays a vital role in the maturation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) from the mice immunized with human β2-glycoprotein I (β2GPI). TLR4 is required for the activation of B cells and the production of autoantibody in mice treated with β2GPI. However, TLR4 provides a third signal for B cell activation and then promotes B cells better receiving signals from both B cell antigen receptor (BCR) and CD40, thus promoting B cell activation, surface molecules expression, anti-β2GPI Ab production, and cytokines secretion and making B cell functioning like an antigen presenting cell (APC). At the same time, TLR4 also promotes B cells producing antibodies by upregulating the expression of B-cell activating factor (BAFF). In this paper, we aim to review the functions of TLR4 in B cell immune response and antibody production in autoimmune disease APS and try to find a new way for the prevention and treatment of APS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of Toll-like receptor 4 on β2-glycoprotein I-induced B cell activation in mouse model.Mol Immunol. 2016 Mar;71:78-86. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2016.01.012. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26872007
-
Effects of Toll-like receptor 4 on β2-glycoprotein I-induced splenic T cell subsets differentiation.Immunol Lett. 2018 Jun;198:17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2018.03.010. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Immunol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29601942
-
TLR4 is involved in the pathogenic effects observed in a murine model of antiphospholipid syndrome.Clin Immunol. 2015 Oct;160(2):198-210. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.05.017. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26065621
-
The role of TLR4 in pathophysiology of antiphospholipid syndrome-associated thrombosis and pregnancy morbidity.Br J Haematol. 2014 Jan;164(2):165-76. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12587. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Br J Haematol. 2014. PMID: 24180619 Review.
-
β2-Glycoprotein I-Reactive T Cells in Autoimmune Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 10;9:2836. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02836. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30619248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short-chain fatty acids: key antiviral mediators of gut microbiota.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 25;16:1614879. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1614879. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40787446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Regulatory B Cells in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy.J Immunol Res. 2020 Dec 21;2020:7638365. doi: 10.1155/2020/7638365. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 33426094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of short-chain fatty acids in inhibiting HDAC and activating p38 MAPK are critical for promoting B10 cell generation and function.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jun 7;12(6):582. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03880-9. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34099635 Free PMC article.
-
From autoinflammation to autoimmunity: old and recent findings.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Sep;37(9):2305-2321. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4209-9. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 30014358 Review.
-
Cytokine-Producing B Cells Promote Immune-Mediated Bile Duct Injury in Murine Biliary Atresia.Hepatology. 2018 Nov;68(5):1890-1904. doi: 10.1002/hep.30051. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Hepatology. 2018. PMID: 29679373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McNeil H. P., Simpson R. J., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Anti-phospholipid antibodies are directed against a complex antigen that includes a lipid-binding inhibitor of coagulation: beta 2-glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H) Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1990;87(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4120. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

