Runx1 Orchestrates Sphingolipid Metabolism and Glucocorticoid Resistance in Lymphomagenesis
- PMID: 27869314
- PMCID: PMC5408393
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.25802
Runx1 Orchestrates Sphingolipid Metabolism and Glucocorticoid Resistance in Lymphomagenesis
Abstract
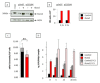
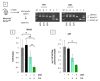
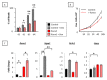
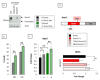
The three-membered RUNX gene family includes RUNX1, a major mutational target in human leukemias, and displays hallmarks of both tumor suppressors and oncogenes. In mouse models, the Runx genes appear to act as conditional oncogenes, as ectopic expression is growth suppressive in normal cells but drives lymphoma development potently when combined with over-expressed Myc or loss of p53. Clues to underlying mechanisms emerged previously from murine fibroblasts where ectopic expression of any of the Runx genes promotes survival through direct and indirect regulation of key enzymes in sphingolipid metabolism associated with a shift in the "sphingolipid rheostat" from ceramide to sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). Testing of this relationship in lymphoma cells was therefore a high priority. We find that ectopic expression of Runx1 in lymphoma cells consistently perturbs the sphingolipid rheostat, whereas an essential physiological role for Runx1 is revealed by reduced S1P levels in normal spleen after partial Cre-mediated excision. Furthermore, we show that ectopic Runx1 expression confers increased resistance of lymphoma cells to glucocorticoid-mediated apoptosis, and elucidate the mechanism of cross-talk between glucocorticoid and sphingolipid metabolism through Sgpp1. Dexamethasone potently induces expression of Sgpp1 in T-lymphoma cells and drives cell death which is reduced by partial knockdown of Sgpp1 with shRNA or direct transcriptional repression of Sgpp1 by ectopic Runx1. Together these data show that Runx1 plays a role in regulating the sphingolipid rheostat in normal development and that perturbation of this cell fate regulator contributes to Runx-driven lymphomagenesis. J. Cell. Biochem. 118: 1432-1441, 2017. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: GLUCOCORTICOID; ONCOGENE; Runx1; SPHINGOLIPID; SURVIVAL.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oncogenic Runx1-Myc axis in p53-deficient thymic lymphoma.Gene. 2022 Apr 20;819:146234. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146234. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35114276
-
Addiction to Runx1 is partially attenuated by loss of p53 in the Eµ-Myc lymphoma model.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 26;7(17):22973-87. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8554. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27056890 Free PMC article.
-
Runx regulation of sphingolipid metabolism and survival signaling.Cancer Res. 2010 Jul 15;70(14):5860-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0726. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20587518 Free PMC article.
-
The Runx genes: lineage-specific oncogenes and tumor suppressors.Oncogene. 2004 May 24;23(24):4308-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207130. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15156187 Review.
-
Sphingolipid signaling and hematopoietic malignancies: to the rheostat and beyond.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Nov;11(9):782-93. doi: 10.2174/187152011797655159. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21707493 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The long noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 controlled by AML1 enhances glucocorticoid resistance by activating RHOA/ROCK1 pathway through suppressing ARHGAP18.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jul 14;12(7):702. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03982-4. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34262023 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation accumulation in cancer genes relates to nonoptimal outcome in chronic myeloid leukemia.Blood Adv. 2020 Feb 11;4(3):546-559. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000943. Blood Adv. 2020. PMID: 32045476 Free PMC article.
-
MYCT1 inhibits hematopoiesis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by suppressing RUNX1 transcription.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Jan 3;29(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00522-0. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38172714 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements on the Multifaceted Roles of Sphingolipids in Hematological Malignancies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 22;23(21):12745. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112745. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sugar symphony: glycosylation in cancer metabolism and stemness.Trends Cell Biol. 2025 May;35(5):412-425. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2024.09.006. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Trends Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39462722 Review.
References
-
- Ben‐Ami O, Friedman D, Leshkowitz D, Goldenberg D, Orlovsky K, Pencovich N, Lotem J, Tanay A, Groner Y. 2013. Addiction of t(8;21) and inv(16) acute myeloid leukemia to native RUNX1. Cell Rep 4:1131–1143. - PubMed
-
- Bhadri VA, Trahair TN, Lock RB. 2012. Glucocorticoid resistance in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. J Paediatr Child Health 48:634–640. - PubMed
-
- Bianchini R, Nocentini G, Krausz LT, Fettucciari K, Coaccioli S, Ronchetti S, Riccardi C. 2006. Modulation of pro‐ and antiapoptotic molecules in double‐positive (CD4 + CD8 +) thymocytes following dexamethasone treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:887–897. - PubMed
-
- Blyth K, Slater N, Hanlon L, Bell M, Mackay N, Stewart M, Neil JC, Cameron ER. 2009. Runx1 promotes B‐cell survival and lymphoma development. Blood Cells Mol Dis 43:12–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/B/000C0419/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- A11951/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 11951/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- BB/H024824/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/B/0000H213/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

