Vertebrate Host Susceptibility to Heartland Virus
- PMID: 27869591
- PMCID: PMC5189141
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2212.160472
Vertebrate Host Susceptibility to Heartland Virus
Abstract
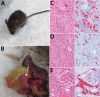
Heartland virus (HRTV) is a recently described phlebovirus initially isolated in 2009 from 2 humans who had leukopenia and thrombocytopenia. Serologic assessment of domestic and wild animal populations near the residence of 1 of these persons showed high exposure rates to raccoons, white-tailed deer, and horses. To our knowledge, no laboratory-based assessments of viremic potential of animals infected with HRTV have been performed. We experimentally inoculated several vertebrates (raccoons, goats, chickens, rabbits, hamsters, C57BL/6 mice, and interferon-α/β/γ receptor-deficient [Ag129]) mice with this virus. All animals showed immune responses against HRTV after primary or secondary exposure. However, neutralizing antibody responses were limited. Only Ag129 mice showed detectable viremia and associated illness and death, which were dose dependent. Ag129 mice also showed development of mean peak viral antibody titers >8 log10 PFU/mL, hemorrhagic hepatic lesions, splenomegaly, and large amounts of HRTV antigen in mononuclear cells and hematopoietic cells in the spleen.
Keywords: Ag129 mice; HRTV; Heartland virus; chickens; goats; hamsters; host susceptibility; mice; mouse model; phlebovirus; rabbits; raccoons; vector-borne infections; vertebrates; virulence; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures

References
-
- Bosco-Lauth AM, Panella NA, Root JJ, Gidlewski T, Lash RR, Harmon JR, et al. Serological investigation of heartland virus (Bunyaviridae: Phlebovirus) exposure in wild and domestic animals adjacent to human case sites in Missouri 2012-2013. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;92:1163–7.10.4269/ajtmh.14-0702 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

