The Role of Individual Disulfide Bonds of μ-Conotoxin GIIIA in the Inhibition of NaV1.4
- PMID: 27869701
- PMCID: PMC5128756
- DOI: 10.3390/md14110213
The Role of Individual Disulfide Bonds of μ-Conotoxin GIIIA in the Inhibition of NaV1.4
Abstract
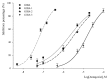
μ-Conotoxin GIIIA, a peptide toxin isolated from Conus geographus, preferentially blocks the skeletal muscle sodium channel NaV1.4. GIIIA folds compactly to a pyramidal structure stabilized by three disulfide bonds. To assess the contributions of individual disulfide bonds of GIIIA to the blockade of NaV1.4, seven disulfide-deficient analogues were prepared and characterized, each with one, two, or three pairs of disulfide-bonded Cys residues replaced with Ala. The inhibitory potency of the analogues against NaV1.4 was assayed by whole cell patch-clamp on rNaV1.4, heterologously expressed in HEK293 cells. The corresponding IC50 values were 0.069 ± 0.005 μM for GIIIA, 2.1 ± 0.3 μM for GIIIA-1, 3.3 ± 0.2 μM for GIIIA-2, and 15.8 ± 0.8 μM for GIIIA-3 (-1, -2 and -3 represent the removal of disulfide bridges Cys3-Cys15, Cys4-Cys20 and Cys10-Cys21, respectively). Other analogues were not active enough for IC50 measurement. Our results indicate that all three disulfide bonds of GIIIA are required to produce effective inhibition of NaV1.4, and the removal of any one significantly lowers its sodium channel binding affinity. Cys10-Cys21 is the most important for the NaV1.4 potency.
Keywords: GIIIA; NaV1.4; disulfide bond; electrophysiology; μ-conotoxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Multiple, distributed interactions of μ-conotoxin PIIIA associated with broad targeting among voltage-gated sodium channels.Biochemistry. 2011 Jan 11;50(1):116-24. doi: 10.1021/bi101316y. Epub 2010 Dec 10. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21110521
-
Roles of basic amino acid residues in the activity of μ-conotoxin GIIIA and GIIIB, peptide blockers of muscle sodium channels.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2015 Apr;85(4):488-93. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12433. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2015. PMID: 25228447
-
NMR Structure of μ-Conotoxin GIIIC: Leucine 18 Induces Local Repacking of the N-Terminus Resulting in Reduced NaV Channel Potency.Molecules. 2018 Oct 22;23(10):2715. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102715. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30360356 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of μ-conotoxins, peptide-based sodium channel blockers with analgesic activity.Future Med Chem. 2014 Oct;6(15):1677-98. doi: 10.4155/fmc.14.107. Future Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25406007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Folding of conotoxins: formation of the native disulfide bridges during chemical synthesis and biosynthesis of Conus peptides.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008 Jan;10(1):141-55. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1856. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008. PMID: 17961068 Review.
Cited by
-
Coagulation Factor XIIIa Inhibitor Tridegin: On the Role of Disulfide Bonds for Folding, Stability, and Function.J Med Chem. 2019 Apr 11;62(7):3513-3523. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01982. Epub 2019 Mar 21. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30852892 Free PMC article.
-
Inherent fast inactivation particle of Nav channels as a new binding site for a neurotoxin.EMBO J. 2025 Jun;44(11):3180-3209. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00438-9. Epub 2025 Apr 22. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 40263599 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Inhibition by µ-Conotoxins.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Jan 18;16(1):55. doi: 10.3390/toxins16010055. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38251271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and synthesis of a clickable, photoreactive amino acid p-(4-(but-3-yn-1-yl)benzoyl)-l-phenylalanine for peptide photoaffinity labeling.RSC Adv. 2023 Jan 4;13(2):866-872. doi: 10.1039/d2ra07248c. eCollection 2023 Jan 3. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36686919 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the disulfide bond on the structure and activity of μ-conotoxin PIIIA in the inhibition of NaV1.4.RSC Adv. 2019 Jan 3;9(2):668-674. doi: 10.1039/c8ra06103c. eCollection 2019 Jan 2. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35517619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Callaghan B., Haythornthwaite A., Berecki G., Clark R.J., Craik D.J., Adams D.J. Analgesic alpha-conotoxins Vc1.1 and Rg1A inhibit N-type calcium channels in rat sensory neurons via GABAB receptor activation. J. Neurosci. 2008;28:10943–10951. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3594-08.2008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

