The Vitamin E Analog Gamma-Tocotrienol (GT3) and Statins Synergistically Up-Regulate Endothelial Thrombomodulin (TM)
- PMID: 27869747
- PMCID: PMC5133932
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17111937
The Vitamin E Analog Gamma-Tocotrienol (GT3) and Statins Synergistically Up-Regulate Endothelial Thrombomodulin (TM)
Abstract
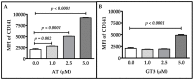
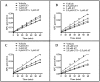
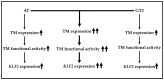
Statins; a class of routinely prescribed cholesterol-lowering drugs; inhibit 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzymeA reductase (HMGCR) and strongly induce endothelial thrombomodulin (TM); which is known to have anti-inflammatory; anti-coagulation; anti-oxidant; and radioprotective properties. However; high-dose toxicity limits the clinical use of statins. The vitamin E family member gamma-tocotrienol (GT3) also suppresses HMGCR activity and induces TM expression without causing significant adverse side effects; even at high concentrations. To investigate the synergistic effect of statins and GT3 on TM; a low dose of atorvastatin and GT3 was used to treat human primary endothelial cells. Protein-level TM expression was measured by flow cytometry. TM functional activity was determined by activated protein C (APC) generation assay. Expression of Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2), one of the key transcription factors of TM, was measured by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). TM expression increased in a dose-dependent manner after both atorvastatin and GT3 treatment. A combined treatment of a low-dose of atorvastatin and GT3 synergistically up-regulated TM expression and functional activity. Finally; atorvastatin and GT3 synergistically increased KLF2 expression. These findings suggest that combined treatment of statins with GT3 may provide significant health benefits in treating a number of pathophysiological conditions; including inflammatory and cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Kruppel-like transcription factors; activated protein C; endothelial cells; gamma-tocotrienol; statins; thrombomodulin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Deanfield J.E., Halcox J.P., Rabelink T.J. Endothelial function and dysfunction: Testing and clinical relevance. Circulation. 2007;115:1285–1295. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

