Contribution of copy number variants to schizophrenia from a genome-wide study of 41,321 subjects
- PMID: 27869829
- PMCID: PMC5737772
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3725
Contribution of copy number variants to schizophrenia from a genome-wide study of 41,321 subjects
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Contribution of copy number variants to schizophrenia from a genome-wide study of 41,321 subjects.Nat Genet. 2017 Mar 30;49(4):651. doi: 10.1038/ng0417-651d. Nat Genet. 2017. PMID: 28358131 No abstract available.
-
Erratum: Contribution of copy number variants to schizophrenia from a genome-wide study of 41,321 subjects.Nat Genet. 2017 Sep 27;49(10):1558. doi: 10.1038/ng1017-1558d. Nat Genet. 2017. PMID: 28951625 No abstract available.
Abstract
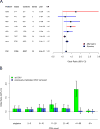
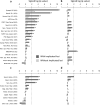
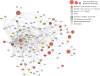
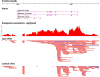
Copy number variants (CNVs) have been strongly implicated in the genetic etiology of schizophrenia (SCZ). However, genome-wide investigation of the contribution of CNV to risk has been hampered by limited sample sizes. We sought to address this obstacle by applying a centralized analysis pipeline to a SCZ cohort of 21,094 cases and 20,227 controls. A global enrichment of CNV burden was observed in cases (odds ratio (OR) = 1.11, P = 5.7 × 10-15), which persisted after excluding loci implicated in previous studies (OR = 1.07, P = 1.7 × 10-6). CNV burden was enriched for genes associated with synaptic function (OR = 1.68, P = 2.8 × 10-11) and neurobehavioral phenotypes in mouse (OR = 1.18, P = 7.3 × 10-5). Genome-wide significant evidence was obtained for eight loci, including 1q21.1, 2p16.3 (NRXN1), 3q29, 7q11.2, 15q13.3, distal 16p11.2, proximal 16p11.2 and 22q11.2. Suggestive support was found for eight additional candidate susceptibility and protective loci, which consisted predominantly of CNVs mediated by nonallelic homologous recombination.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH095034/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH077139/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K013807/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 MH094411/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RP-PG-0606-1049/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- G1100583/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0700995/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 MH109514/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0901310/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 MH094421/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH109528/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/P005748/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K004867/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 MH109536/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH109501/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0600972/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH085548/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 MH109539/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- PDA/02/06/016/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MR/L023784/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

