Antizyme inhibitor 1: a potential carcinogenic molecule
- PMID: 27870265
- PMCID: PMC5329145
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13122
Antizyme inhibitor 1: a potential carcinogenic molecule
Abstract
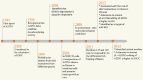
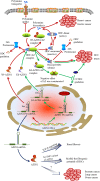
Polyamines are multivalent and organic cations essential for cellular growth, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Increased levels of polyamines are closely associated with numerous forms of cancer. An autoregulatory circuit composed of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), antizyme (AZ) and antizyme inhibitor (AZI) govern the intracellular level of polyamines. Antizyme binds with ODC to inhibit ODC activity and to promote the ubiquitin-independent degradation of ODC. Antizyme inhibitor binds to AZ with a higher affinity than ODC. Consequently, ODC is released from the ODC-AZ complex to rescue its activity. Antizyme inhibitor increases the ODC activity to accelerate the formation of intracellular polyamines, triggering gastric and breast carcinogenesis as well as hepatocellular carcinoma and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development. Antizyme inhibitor 1 (AZIN1), a primary member of the AZI family, has aroused more attention because of its contribution to cancer. Even though its conformation is changed by adenosine-to-inosine (A→I) RNA editing, it plays an important role in tumorigenesis through regulating intracellular polyamines. Encouragingly, AZIN1 has been revealed to have an additional function outside the polyamine pathway so as to bypass the deficiency of targeting the polyamine biosynthetic pathway, promising to become a critical target for cancer therapy. Here, we review the latest research advances into AZIN1 and its potential contribution to carcinogenesis.
Keywords: Antizyme; antizyme inhibitor 1; carcinogenesis; ornithine decarboxylase; polyamine.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
-
- Pegg AE. Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 14529–32. - PubMed
-
- Kahana C, Asher G, Shaul Y. Mechanisms of protein degradation: an odyssey with ODC. Cell Cycle 2005; 4: 1461–4. - PubMed
-
- Gerner EW, Meyskens FL. Polyamines and cancer: old molecules, new understanding. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 781–92. - PubMed
-
- Snapir Z, Keren‐Paz A, Bercovich Z, Kahana C. Antizyme 3 inhibits polyamine uptake and ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) activity, but does not stimulate ODC degradation. Biochem J 2009; 419: 99–103, 101 p following 103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

