Evaluating mesenchymal stem cell therapy for sepsis with preclinical meta-analyses prior to initiating a first-in-human trial
- PMID: 27870924
- PMCID: PMC5153252
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.17850
Evaluating mesenchymal stem cell therapy for sepsis with preclinical meta-analyses prior to initiating a first-in-human trial
Abstract
Evaluation of preclinical evidence prior to initiating early-phase clinical studies has typically been performed by selecting individual studies in a non-systematic process that may introduce bias. Thus, in preparation for a first-in-human trial of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) for septic shock, we applied systematic review methodology to evaluate all published preclinical evidence. We identified 20 controlled comparison experiments (980 animals from 18 publications) of in vivo sepsis models. Meta-analysis demonstrated that MSC treatment of preclinical sepsis significantly reduced mortality over a range of experimental conditions (odds ratio 0.27, 95% confidence interval 0.18-0.40, latest timepoint reported for each study). Risk of bias was unclear as few studies described elements such as randomization and no studies included an appropriately calculated sample size. Moreover, the presence of publication bias resulted in a ~30% overestimate of effect and threats to validity limit the strength of our conclusions. This novel prospective application of systematic review methodology serves as a template to evaluate preclinical evidence prior to initiating first-in-human clinical studies.
Keywords: epidemiology; global health; human biology; medicine; mouse; preclinical; rat; sepsis; stem cells; systematic review; translation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
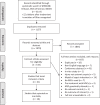
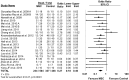
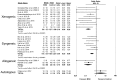



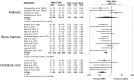


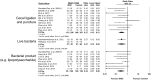

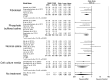


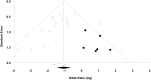
References
-
- Bi L-K, Tang B, Zhu B, Xie C-L, Li S, Lin T-X, Hunag J, Zhang W, Zhu J-Y. Systemic delivery of IL-10 by bone marrow derived stromal cells has therapeutic benefits in sepsis therapy*. Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2010;37:678–685. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1206.2010.00107. - DOI
-
- Canadian Institutes of Health Research RCT Evaluation Criteria and Headings. 2016 http://www.cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/39187.html
-
- Chang CL, Leu S, Sung HC, Zhen YY, Cho CL, Chen A, Tsai TH, Chung SY, Chai HT, Sun CK, Yen CH, Yip HK. Impact of apoptotic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on attenuating organ damage and reducing mortality in rat sepsis syndrome induced by cecal puncture and ligation. Journal of Translational Medicine. 2012;10:244. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

