Inhibition of STAT3- and MAPK-dependent PGE2 synthesis ameliorates phagocytosis of fibrillar β-amyloid peptide (1-42) via EP2 receptor in EMF-stimulated N9 microglial cells
- PMID: 27871289
- PMCID: PMC5117690
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0762-9
Inhibition of STAT3- and MAPK-dependent PGE2 synthesis ameliorates phagocytosis of fibrillar β-amyloid peptide (1-42) via EP2 receptor in EMF-stimulated N9 microglial cells
Abstract
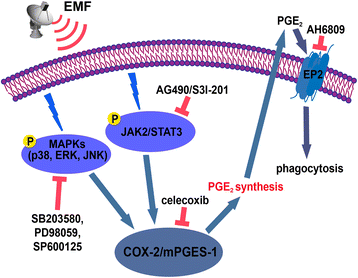
Background: Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-involved neuroinflammatory processes are prevalent in several neurological conditions and diseases. Amyloid burden is correlated with the activation of E-prostanoid (EP) 2 receptors by PGE2 in Alzheimer's disease. We previously demonstrated that electromagnetic field (EMF) exposure can induce pro-inflammatory responses and the depression of phagocytosis in microglial cells, but the signaling pathways involved in phagocytosis of fibrillar β-amyloid (fAβ) in microglial cells exposed to EMF are poorly understood. Given the important role of PGE2 in neural physiopathological processes, we investigated the PGE2-related signaling mechanism in the immunomodulatory phagocytosis of EMF-stimulated N9 microglial cells (N9 cells).
Methods: N9 cells were exposed to EMF with or without pretreatment with the selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), Janus kinase 2 (JAK2), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and antagonists of PG receptors EP1-4. The production of endogenous PGE2 was quantified by enzyme immunoassays. The phagocytic ability of N9 cells was evaluated based on the fluorescence intensity of the engulfed fluorescent-labeled fibrillar β-amyloid peptide (1-42) (fAβ42) measured using a flow cytometer and a fluorescence microscope. The effects of pharmacological agents on EMF-activated microglia were investigated based on the expressions of JAK2, STAT3, p38/ERK/JNK MAPKs, COX-2, microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1), and EP2 using real-time PCR and/or western blotting.
Results: EMF exposure significantly increased the production of PGE2 and decreased the phagocytosis of fluorescent-labeled fAβ42 by N9 cells. The selective inhibitors of COX-2, JAK2, STAT3, and MAPKs clearly depressed PGE2 release and ameliorated microglial phagocytosis after EMF exposure. Pharmacological agents suppressed the phosphorylation of JAK2-STAT3 and MAPKs, leading to the amelioration of the phagocytic ability of EMF-stimulated N9 cells. Antagonist studies of EP1-4 receptors showed that EMF depressed the phagocytosis of fAβ42 through the PGE2 system, which is linked to EP2 receptors.
Conclusions: This study indicates that EMF exposure could induce phagocytic depression via JAK2-STAT3- and MAPK-dependent PGE2-EP2 receptor signaling pathways in microglia. Therefore, pharmacological inhibition of PGE2 synthesis and EP2 receptors may be a potential therapeutic strategy to combat the neurobiological deterioration that follows EMF exposure.
Keywords: EMF; Microglia; PGE2; Phagocytosis; Synthesis.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Curcumin Ameliorates the Reduction Effect of PGE2 on Fibrillar β-Amyloid Peptide (1-42)-Induced Microglial Phagocytosis through the Inhibition of EP2-PKA Signaling in N9 Microglial Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 29;11(1):e0147721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147721. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26824354 Free PMC article.
-
The amelioration of phagocytic ability in microglial cells by curcumin through the inhibition of EMF-induced pro-inflammatory responses.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Mar 19;11:49. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-49. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24645646 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the JAK2-STAT3 pathway in pro-inflammatory responses of EMF-stimulated N9 microglial cells.J Neuroinflammation. 2010 Sep 9;7:54. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-54. J Neuroinflammation. 2010. PMID: 20828402 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of prostanoid synthesis in microglial cells and effects of prostaglandin E2 on microglial functions.Biochimie. 1998 Nov;80(11):899-904. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(00)88886-0. Biochimie. 1998. PMID: 9893949 Review.
-
Microglial EP2 as a new target to increase amyloid beta phagocytosis and decrease amyloid beta-induced damage to neurons.Brain Pathol. 2005 Apr;15(2):134-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2005.tb00509.x. Brain Pathol. 2005. PMID: 15912885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electromagnetic Field Stimulation Therapy for Alzheimer's Disease.Neurology (Chic). 2024;3(1):1020. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Neurology (Chic). 2024. PMID: 38699565 Free PMC article.
-
Comorbidity Genes of Alzheimer's Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Associated with Memory and Cognitive Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 12;25(4):2211. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042211. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Propofol Mediated Protection of the Brain From Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through the Regulation of Microglial Connexin 43.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 8;9:637233. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.637233. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34169070 Free PMC article.
-
Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress-Biological Effects and Consequences for Health.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 6;22(7):3772. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073772. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33917298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PGE2 inhibits neutrophil phagocytosis through the EP2R-cAMP-PTEN pathway.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022 Jul;10(7):e662. doi: 10.1002/iid3.662. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022. PMID: 35759236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlbom A, Bridges J, de Seze R, Hillert L, Juutilainen J, Mattsson MO, Neubauer G, Schuz J, Simko M, Bromen K. Possible effects of electromagnetic fields (EMF) on human health—opinion of the scientific committee on emerging and newly identified health risks (SCENIHR) Toxicology. 2008;246:248–50. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2008.02.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

