The association between intra- and juxta-cortical pathology and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis by quantitative T2* mapping at 7 T MRI
- PMID: 27872810
- PMCID: PMC5107649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.11.001
The association between intra- and juxta-cortical pathology and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis by quantitative T2* mapping at 7 T MRI
Abstract
Using quantitative T2* at 7 Tesla (T) magnetic resonance imaging, we investigated whether impairment in selective cognitive functions in multiple sclerosis (MS) can be explained by pathology in specific areas and/or layers of the cortex. Thirty-one MS patients underwent neuropsychological evaluation, acquisition of 7 T multi-echo T2* gradient-echo sequences, and 3 T anatomical images for cortical surfaces reconstruction. Seventeen age-matched healthy subjects served as controls. Cortical T2* maps were sampled at various depths throughout the cortex and juxtacortex. Relation between T2*, neuropsychological scores and a cognitive index (CI), calculated from a principal component analysis on the whole battery, was tested by a general linear model. Cognitive impairment correlated with T2* increase, independently from white matter lesions and cortical thickness, in cortical areas highly relevant for cognition belonging to the default-mode network (p < 0.05 corrected). Dysfunction in different cognitive functions correlated with longer T2* in selective cortical regions, most of which showed longer T2* relative to controls. For most tests, this association was strongest in deeper cortical layers. Executive dysfunction, however, was mainly related with pathology in juxtameningeal cortex. T2* explained up to 20% of the variance of the CI, independently of conventional imaging metrics (adjusted-R2: 52-67%, p < 5.10- 4). Location of pathology across the cortical width and mantle showed selective correlation with impairment in differing cognitive domains. These findings may guide studies at lower field strength designed to develop surrogate markers of cognitive impairment in MS.
Keywords: 7 Tesla MRI; BVMT - DR, brief visuo-spatial memory test delayed recall; BVMT, brief visual memory test; CI, cognitive index; CVLT, California verbal learning test; Cognitive impairment; DB, digit span backward; DF, digit span forward; DR, delayed recall; EDSS, expanded disability status score; JLOT, judgment of line orientation test; LDCR, long delayed cued recall; LDFR, long delayed free recall; Laminar cortical pathology; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MS, multiple sclerosis; Multiple sclerosis; NP, neuropsychological; PCA, principal component analysis; SDMT, symbol digit modalities test; T2*; TMT, trail making test; TOT, total recall; WCST, Wisconsin card sorting test; WM, white matter; WMLV, white matter lesion volume; q-T2*, quantitative T2*.
Figures
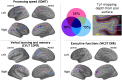
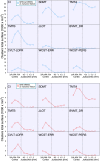
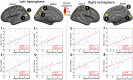
Similar articles
-
Detection and quantification of regional cortical gray matter damage in multiple sclerosis utilizing gradient echo MRI.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Aug 18;9:164-75. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.08.003. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 27330979 Free PMC article.
-
A gradient in cortical pathology in multiple sclerosis by in vivo quantitative 7 T imaging.Brain. 2015 Apr;138(Pt 4):932-45. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv011. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25681411 Free PMC article.
-
Thalamic-hippocampal-prefrontal disruption in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Dec 27;8:440-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.12.015. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 26106524 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical pathology and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis.Expert Rev Neurother. 2011 Mar;11(3):425-32. doi: 10.1586/ern.10.155. Expert Rev Neurother. 2011. PMID: 21375447 Review.
-
Cognitive performance and magnetic resonance imaging in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2024 Aug;88:105705. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2024.105705. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2024. PMID: 38885600
Cited by
-
Laboratory and Neuroimaging Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Where Do We Stand, Where To Go?Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Dec 4;5:340. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00340. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30564579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Voxel-based analysis of gray matter relaxation rates shows different correlation patterns for cognitive impairment and physical disability in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;26:102201. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102201. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32062567 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques in Multiple Sclerosis Clinical Trials.Neurotherapeutics. 2017 Oct;14(4):905-923. doi: 10.1007/s13311-017-0561-8. Neurotherapeutics. 2017. PMID: 28770481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cortical quantitative MRI parameters are related to the cognitive status in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.Eur Radiol. 2020 Feb;30(2):1045-1053. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06437-9. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31602513
-
Functional Components of Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Investigation.Front Neurol. 2017 Nov 28;8:643. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00643. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 29234305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander M.P., Stuss D.T., Fansabedian N. California verbal learning test: performance by patients with focal frontal and non-frontal lesions. Brain. 2003;126:1493–1503. - PubMed
-
- Amato M.P., Bartolozzi M.L., Zipoli V., Portaccio E., Mortilla M., Guidi L., Siracusa G., Sorbi S., Federico A., De Stefano N. Neocortical volume decrease in relapsing-remitting MS patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology. 2004;63:89–93. - PubMed
-
- Benedict R.H., Bruce J.M., Dwyer M.G., Abdelrahman N., Hussein S., Weinstock-Guttman B., Garg N., Munschauer F., Zivadinov R. Neocortical atrophy, third ventricular width, and cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 2006;63:1301–1306. - PubMed
-
- Brissart H., Morele E., Baumann C., Perf M.L., Leininger M., Taillemite L., Dillier C., Pittion S., Spitz E., Debouverie M. Cognitive impairment among different clinical courses of multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Res. 2013;35:867–872. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese M., Agosta F., Rinaldi F., Mattisi I., Grossi P., Favaretto A., Atzori M., Bernardi V., Barachino L., Rinaldi L., Perini P., Gallo P., Filippi M. Cortical lesions and atrophy associated with cognitive impairment in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 2009;66:1144–1150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

