Roles of Zinc Signaling in the Immune System
- PMID: 27872866
- PMCID: PMC5107842
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/6762343
Roles of Zinc Signaling in the Immune System
Abstract
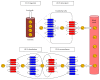
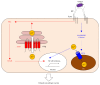
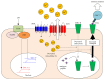
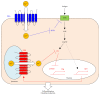
Zinc (Zn) is an essential micronutrient for basic cell activities such as cell growth, differentiation, and survival. Zn deficiency depresses both innate and adaptive immune responses. However, the precise physiological mechanisms of the Zn-mediated regulation of the immune system have been largely unclear. Zn homeostasis is tightly controlled by the coordinated activity of Zn transporters and metallothioneins, which regulate the transport, distribution, and storage of Zn. There is growing evidence that Zn behaves like a signaling molecule, facilitating the transduction of a variety of signaling cascades in response to extracellular stimuli. In this review, we highlight the emerging functional roles of Zn and Zn transporters in immunity, focusing on how crosstalk between Zn and immune-related signaling guides the normal development and function of immune cells.
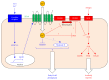
Figures


References
-
- Shankar A. H., Prasad A. S. Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 1998;68(2):447S–463S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

