Estimating Long-Term Survival of Adults with Philadelphia Chromosome-Negative Relapsed/Refractory B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated with Blinatumomab Using Historical Data
- PMID: 27873237
- PMCID: PMC5216100
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-016-0447-x
Estimating Long-Term Survival of Adults with Philadelphia Chromosome-Negative Relapsed/Refractory B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated with Blinatumomab Using Historical Data
Abstract
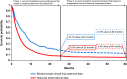
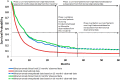
Introduction: Blinatumomab is a bispecific T cell-engaging antibody construct indicated for adult patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) Ph(-) B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), an aggressive disease with poor prognosis. A phase 2 single-arm clinical study showed that 43% of patients achieved CR/CRh within two cycles and approximately 20% of patients receiving blinatumomab were still alive after 2 years.
Methods: The objective of the current analysis was to estimate long-term survival of patients receiving blinatumomab beyond the observed time period in the clinical study using a large historical observational dataset. Conditional survival probabilities of blinatumomab-treated patients beyond month 60 were assumed to be the same as the US general population.
Results: At month 60, the estimated proportion of blinatumomab-treated patients alive was more than double that of historical patients (12.6% vs 5.4%). The mean overall survival was 76.1 months for blinatumomab patients and 39.8 months for historical patients. Sensitivity analyses including additional follow-up data from the clinical study showed consistent results.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that blinatumomab provides substantial overall survival benefit to patients with (R/R) Ph(-) B-precursor ALL compared with salvage chemotherapy.
Funding: Amgen.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01466179 and NCT02003612.
Keywords: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Blinatumomab; Hematology; Long-term survival; Oncology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and activity of blinatumomab for adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2015 Jan;16(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71170-2. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Lancet Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25524800 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term follow-up of blinatumomab in patients with relapsed/refractory Philadelphia chromosome-positive B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Final analysis of ALCANTARA study.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Mar;146:107-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.12.022. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33588145 Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-effectiveness of blinatumomab versus salvage chemotherapy in relapsed or refractory Philadelphia-chromosome-negative B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia from a US payer perspective.J Med Econ. 2017 Sep;20(9):911-922. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2017.1344127. Epub 2017 Jul 11. J Med Econ. 2017. PMID: 28631497 Clinical Trial.
-
Blinatumomab for the Treatment of Philadelphia Chromosome-Negative, Precursor B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Oct 1;21(19):4262-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0125. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26283683 Review.
-
A Systematic Review of Blinatumomab in the Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Engaging an Old Problem With New Solutions.Ann Pharmacother. 2021 Oct;55(10):1236-1253. doi: 10.1177/1060028020988411. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Ann Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33435716
Cited by
-
The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immunotherapy for the treatment of acute leukemia.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Oct;8(2):e000810. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000810. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33077513 Free PMC article.
-
T cell-redirecting bispecific antibodies in cancer immunotherapy: recent advances.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Apr;145(4):941-956. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02867-6. Epub 2019 Feb 23. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30798356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syk inhibitors in clinical development for hematological malignancies.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jul 28;10(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0512-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28754125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances on blinatumomab for acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2019 Nov 6;8:28. doi: 10.1186/s40164-019-0152-y. eCollection 2019. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31709129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotargeting relapsed or refractory precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia - role of blinatumomab.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Jul 19;10:3567-3578. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S103470. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28790849 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical