The impact of transposable elements on mammalian development
- PMID: 27875251
- PMCID: PMC5830075
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.132639
The impact of transposable elements on mammalian development
Abstract
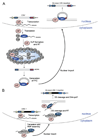
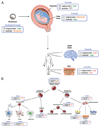
Despite often being classified as selfish or junk DNA, transposable elements (TEs) are a group of abundant genetic sequences that have a significant impact on mammalian development and genome regulation. In recent years, our understanding of how pre-existing TEs affect genome architecture, gene regulatory networks and protein function during mammalian embryogenesis has dramatically expanded. In addition, the mobilization of active TEs in selected cell types has been shown to generate genetic variation during development and in fully differentiated tissues. Importantly, the ongoing domestication and evolution of TEs appears to provide a rich source of regulatory elements, functional modules and genetic variation that fuels the evolution of mammalian developmental processes. Here, we review the functional impact that TEs exert on mammalian developmental processes and discuss how the somatic activity of TEs can influence gene regulatory networks.
Keywords: Endogenous retrovirus; Genetic variation; Genome regulation; LINE-1; Retrotransposon.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bejerano G, Lowe CB, Ahituv N, King B, Siepel A, Salama SR, Rubin EM, Kent WJ, Haussler D. A distal enhancer and an ultraconserved exon are derived from a novel retroposon. Nature. 2006;441:87–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

