Multifunctional nanoassemblies of block copolymers for future cancer therapy
- PMID: 27877324
- PMCID: PMC5090551
- DOI: 10.1088/1468-6996/11/1/014109
Multifunctional nanoassemblies of block copolymers for future cancer therapy
Abstract
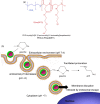
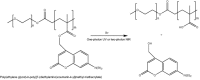
Nanoassemblies from amphiphilic block copolymers are promising nanomedicine platforms for cancer diagnosis and therapy due to their relatively small size, high loading capacity of drugs, controlled drug release, in vivo stability and prolonged blood circulation. Recent clinical trials with self-assembled polymeric micelles incorporating anticancer drugs have shown improved antitumor activity and decreased side effects encouraging the further development of nanoassemblies for drug delivery. This review summarizes recent approaches considering stimuli-responsive, multifunctionality and more advanced architectures, such as vesicles or worm-like micelles, for tumor-specific drug and gene delivery.
Keywords: block copolymers; cancer; drug delivery; gene delivery; self-assembly.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Structural modifications in polymeric micelles to impart multifunctionality for improved drug delivery.Ther Deliv. 2016;7(2):73-87. doi: 10.4155/tde.15.90. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Ther Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26769002 Review.
-
Structural Engineering of Biodegradable PCL Block Copolymer Nanoassemblies for Enzyme-Controlled Drug Delivery in Cancer Cells.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2016 Nov 14;2(11):1926-1941. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00310. Epub 2016 Sep 30. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2016. PMID: 33440528
-
Polymer nanoassemblies for cancer treatment and imaging.Ther Deliv. 2010 Dec;1(6):803-17. doi: 10.4155/tde.10.70. Ther Deliv. 2010. PMID: 22834015 Review.
-
Stimulus-Responsive Degradable Polylactide-Based Block Copolymer Nanoassemblies for Controlled/Enhanced Drug Delivery.Mol Pharm. 2017 Aug 7;14(8):2460-2474. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00284. Epub 2017 May 23. Mol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28493712
-
Synthesis of enzyme-responsive theranostic amphiphilic conjugated bottlebrush copolymers for enhanced anticancer drug delivery.Acta Biomater. 2022 May;144:15-31. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.03.028. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35306183
Cited by
-
Structurally nanoengineered antimicrobial peptide polymers: design, synthesis and biomedical applications.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jul 19;37(8):139. doi: 10.1007/s11274-021-03109-z. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34278535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of biocompatible alginate- and deferoxamine-coated ternary composites for magnetic resonance imaging and gene delivery into glioblastoma cells.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2015 Jun;5(3):382-91. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2015.03.12. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2015. PMID: 26029641 Free PMC article.
-
Ternary hybrid nanocomposites for gene delivery and magnetic resonance imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2013 Dec;3(6):302-7. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2013.12.05. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2013. PMID: 24404444 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical differences between block copolymer self-assembled and cross-linked nanoassemblies as carriers for tunable drug release.Pharm Res. 2013 Feb;30(2):478-88. doi: 10.1007/s11095-012-0893-3. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 23054094
-
Antiviral Lipid Nanocarrier Loaded with Remdesivir Effective Against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro Model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Mar 27;18:1561-1575. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S391462. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37007987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsumura Y. and Maeda H. Cancer Res. 1986;46:6387. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
