One-pot synthesis of magnetic, macro/mesoporous bioactive glasses for bone tissue engineering
- PMID: 27877572
- PMCID: PMC5074375
- DOI: 10.1088/1468-6996/14/2/025004
One-pot synthesis of magnetic, macro/mesoporous bioactive glasses for bone tissue engineering
Abstract
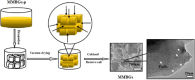
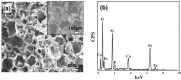
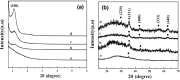
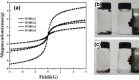
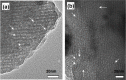
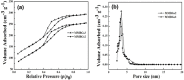
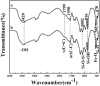
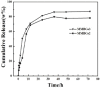
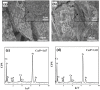
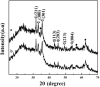
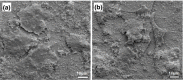
Magnetic and macro/mesoporous bioactive glasses were synthesized by a one-pot method via a handy salt leaching technique. It was identified to be an effective and simple synthetic strategy. The non-ionic triblock copolymer, poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(propylene glycol)-block-poly(ethylene glycol) (P123), was used as the structure directing agent for mesoporous structure but also as the reductant to reduce the iron source into magnetic iron oxide. The prepared materials exhibited excellent super-paramagnetic property with interconnected macroporous (200-300 μm) and mesoporous (3.4 nm) structure. Furthermore, their outstanding drug storage/release properties and rapid (5) induction of hydroxyapatite growth ability were investigated after immersing in simulated body fluid solution at 37 °C. Notably, the biocompatibility assessment confirmed that the materials obtained presented good biocompatibility and enhanced adherence of HeLa cells. Herein, the novel materials are expected to have potential application for bone tissue engineering.
Keywords: 10.03; 10.09; 20.03; bioactive glasses; bone tissue engineering; drug delivery; magnetic; porous.
Figures
Similar articles
-
One-pot synthesis of macro-mesoporous bioactive glasses/polylactic acid for bone tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014 Oct;43:367-74. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2014.07.042. Epub 2014 Jul 19. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014. PMID: 25175225
-
Synthesis of magnetic, macro/mesoporous bioactive glasses based on coral skeleton for bone tissue engineering.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2014 Dec;8(4):275-81. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2013.0056. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25429508
-
Hierarchical porous bioactive glasses/PLGA-magnetic SBA-15 for dual-drug release.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014 Jun 1;39:21-8. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2014.01.060. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014. PMID: 24863192
-
Bioactive glass-based materials with hierarchical porosity for medical applications: Review of recent advances.Acta Biomater. 2016 Sep 15;42:18-32. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.06.033. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 27370907 Review.
-
Mesoporous bioactive glasses for bone healing and biomolecules delivery.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Jan;106:110180. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110180. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 31753410 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements in mesoporous bioactive glasses for effective bone cancer therapy: Recent developments and future perspectives.Biomater Biosyst. 2025 Feb 15;17:100108. doi: 10.1016/j.bbiosy.2025.100108. eCollection 2025 Mar. Biomater Biosyst. 2025. PMID: 40083816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering mesoporous bioactive glasses for emerging stimuli-responsive drug delivery and theranostic applications.Bioact Mater. 2024 Jan 12;34:436-462. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.01.001. eCollection 2024 Apr. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38282967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prospective opportunities offered by magnetic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: a review.Joints. 2017 Feb 7;4(4):228-235. doi: 10.11138/jts/2016.4.4.228. eCollection 2016 Oct-Dec. Joints. 2017. PMID: 28217659 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
