Non-metallic nanomaterials in cancer theranostics: a review of silica- and carbon-based drug delivery systems
- PMID: 27877592
- PMCID: PMC5090318
- DOI: 10.1088/1468-6996/14/4/044407
Non-metallic nanomaterials in cancer theranostics: a review of silica- and carbon-based drug delivery systems
Abstract
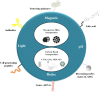
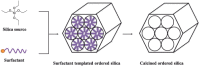
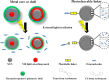
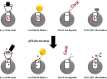
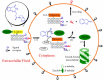
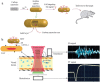
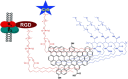
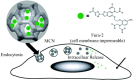
The rapid development in nanomaterials has brought great opportunities to cancer theranostics, which aims to combine diagnostics and therapy for cancer treatment and thereby improve the healthcare of patients. In this review we focus on the recent progress of several cancer theranostic strategies using mesoporous silica nanoparticles and carbon-based nanomaterials. Silicon and carbon are both group IV elements; they have been the most abundant and significant non-metallic substances in human life. Their intrinsic physical/chemical properties are of critical importance in the fabrication of multifunctional drug delivery systems. Responsive nanocarriers constructed using these nanomaterials have been promising in cancer-specific theranostics during the past decade. In all cases, either a controlled texture or the chemical functionalization is coupled with adaptive properties, such as pH-, light-, redox- and magnetic field- triggered responses. Several studies in cells and mice models have implied their underlying therapeutic efficacy; however, detailed and long-term in vivo clinical evaluations are certainly required to make these bench-made materials compatible in real bedside circumstances.
Keywords: carbon-based nanomaterials; drug delivery systems; mesoporous silica nanoparticles; theranostics.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mesoporous Silica Nanomaterials: Versatile Nanocarriers for Cancer Theranostics and Drug and Gene Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Feb 13;11(2):77. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11020077. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 30781850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical imaging and anticancer chemotherapy through carbon dot created hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles.Acta Biomater. 2017 Jun;55:466-480. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.03.054. Epub 2017 Apr 1. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28373086
-
Redox-responsive theranostic nanoplatforms based on inorganic nanomaterials.J Control Release. 2017 Aug 10;259:40-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.03.018. Epub 2017 Mar 10. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28288893 Review.
-
Recent Advancement of Nanotheranostics in Cancer Applications.Curr Drug Deliv. 2024 May 29. doi: 10.2174/0115672018307617240514092110. Online ahead of print. Curr Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 38812425
-
Multifunctional Redox-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Efficient Targeting Drug Delivery and Magnetic Resonance Imaging.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016 Dec 14;8(49):33829-33841. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b11802. Epub 2016 Nov 30. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016. PMID: 27960384
Cited by
-
A Review on Drug Delivery System for Tumor Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 4;12:735446. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.735446. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34675807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photoluminescence and doping mechanism of theranostic Eu3+/Fe3+ dual-doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2014 Sep 23;15(5):055005. doi: 10.1088/1468-6996/15/5/055005. eCollection 2014 Oct. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2014. PMID: 27877717 Free PMC article.
-
In light-sensitive drug delivery system nanoparticles mediate oxidative stress.Am J Transl Res. 2020 May 15;12(5):1469-1480. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32509156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Nano Neuroscience: From Nanomaterials to Nanotools.Front Neurosci. 2019 Jan 15;12:953. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00953. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30697140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Agricultural and Biomedical Applications of Chitosan-Based Nanomaterials.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Sep 24;10(10):1903. doi: 10.3390/nano10101903. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32987697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paciotti G F, Kingston D G I. and Tamarkin L. Colloidal gold nanoparticles: a novel nanoparticle platform for developing multifunctional tumor-targeted drug delivery vectors. Drug Dev. Res. 2006;67:47–54. doi: 10.1002/ddr.20066. - DOI
-
- Slowing I I, Trewyn B G, Giri S. and Lin V S Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery and biosensing applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007;17:1225–36. doi: 10.1002/adfm.200601191. - DOI
-
- Soppimath K S, Tan D C. and Yang Y Y. pH-triggered thermally responsive polymer core–shell nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2005;17:318–23. doi: 10.1002/adma.200401057. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
