Recombinant Haplotypes Narrow the ARMS2/HTRA1 Association Signal for Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- PMID: 27879347
- PMCID: PMC5289859
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.116.195966
Recombinant Haplotypes Narrow the ARMS2/HTRA1 Association Signal for Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Abstract
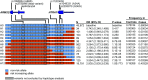
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of blindness in ageing societies, triggered by both environmental and genetic factors. The strongest genetic signal for AMD with odds ratios of up to 2.8 per adverse allele was found previously over a chromosomal region in 10q26 harboring two genes, ARMS2 and HTRA1, although with little knowledge as to which gene or genetic variation is functionally relevant to AMD pathology. In this study, we analyzed rare recombinant haplotypes in 16,144 AMD cases and 17,832 controls from the International AMD Genomics Consortium and identified variants in ARMS2 but not HTRA1 to exclusively carry the AMD risk with P-values between 1.0 × 10-773 and 6.7 × 10-5 This now allows prioritization of the gene of interest for subsequent functional studies.
Keywords: ARMS2/HTRA1 gene locus; age-related macular degeneration; genetic association studies; haplotypes; linkage disequilibrium.
Copyright © 2017 Grassmann et al.
Figures
References
-
- Dewan A., Liu M., Hartman S., Zhang S. S.-M., Liu D. T. L., et al. , 2006. HTRA1 promoter polymorphism in wet age-related macular degeneration. Science 314: 989–992. - PubMed
-
- Friedrich U., Datta S., Schubert T., Plössl K., Schneider M., et al. , 2015. Synonymous variants in HTRA1 implicated in AMD susceptibility impair its capacity to regulate TGF-β signaling. Hum. Mol. Genet. 24: 6361–6373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

