Natural Variation of Molecular and Morphological Gibberellin Responses
- PMID: 27879393
- PMCID: PMC5210761
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.16.01626
Natural Variation of Molecular and Morphological Gibberellin Responses
Abstract
Although phytohormones such as gibberellins are essential for many conserved aspects of plant physiology and development, plants vary greatly in their responses to these regulatory compounds. Here, we use genetic perturbation of endogenous gibberellin levels to probe the extent of intraspecific variation in gibberellin responses in natural accessions of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). We find that these accessions vary greatly in their ability to buffer the effects of overexpression of GA20ox1, encoding a rate-limiting enzyme for gibberellin biosynthesis, with substantial differences in bioactive gibberellin concentrations as well as transcriptomes and growth trajectories. These findings demonstrate a surprising level of flexibility in the wiring of regulatory networks underlying hormone metabolism and signaling.
© 2017 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
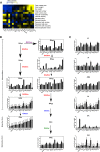
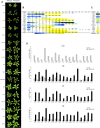


References
-
- Andriankaja M, Dhondt S, De Bodt S, Vanhaeren H, Coppens F, De Milde L, Mühlenbock P, Skirycz A, Gonzalez N, Beemster GTS, Inzé D (2012) Exit from proliferation during leaf development in Arabidopsis thaliana: a not-so-gradual process. Dev Cell 22: 64–78 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

