Hydrogen Induced Abrupt Structural Expansion at High Temperatures of a Ni32Nb28Zr30Cu10 Membrane for H₂ Purification
- PMID: 27879641
- PMCID: PMC5192404
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes6040048
Hydrogen Induced Abrupt Structural Expansion at High Temperatures of a Ni32Nb28Zr30Cu10 Membrane for H₂ Purification
Abstract
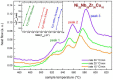
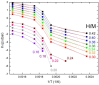
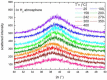
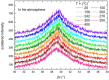
Ni-Nb-Zr amorphous membranes, prepared by melt-spinning, show great potential for replacing crystalline Pd-based materials in the field of hydrogen purification to an ultrapure grade (>99.999%). In this study, we investigate the temperature evolution of the structure of an amorphous ribbon with the composition Ni32Nb28Zr30Cu10 (expressed in atom %) by means of XRD and DTA measurements. An abrupt structural expansion is induced between 240 and 300 °C by hydrogenation. This structural modification deeply modifies the hydrogen sorption properties of the membrane, which indeed shows a strong reduction of the hydrogen capacity above 270 °C.
Keywords: DTA; XRD; amorphous membranes; hydrogen sorption; hydrogenation enthalpy; lattice expansion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Paglieri S., Way J.D. Innovations in palladium membrane research. Sep. Purif. Methods. 2002;31:1–169. doi: 10.1081/SPM-120006115. - DOI
-
- Adhikari S., Fernando S. Hydrogen Membrane Separation Techniques. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006;45:875–881. doi: 10.1021/ie050644l. - DOI
-
- Tosti S., Bettinali L., Violante V. Rolled thin Pd and Pd-Ag membranes for hydrogen separation and production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 2000;25:319–325. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3199(99)00044-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

