Interplay of cis- and trans-regulatory mechanisms in the spliceosomal RNA helicase Brr2
- PMID: 27880071
- PMCID: PMC5270545
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1255384
Interplay of cis- and trans-regulatory mechanisms in the spliceosomal RNA helicase Brr2
Abstract
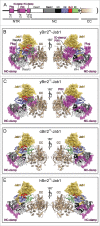
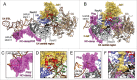
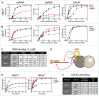
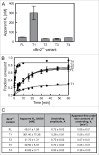
RNA helicase Brr2 is implicated in multiple phases of pre-mRNA splicing and thus requires tight regulation. Brr2 can be auto-inhibited via a large N-terminal region folding back onto its helicase core and auto-activated by a catalytically inactive C-terminal helicase cassette. Furthermore, it can be regulated in trans by the Jab1 domain of the Prp8 protein, which can inhibit Brr2 by intermittently inserting a C-terminal tail in the enzyme's RNA-binding tunnel or activate the helicase after removal of this tail. Presently it is unclear, whether these regulatory mechanisms functionally interact and to which extent they are evolutionarily conserved. Here, we report crystal structures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Chaetomium thermophilum Brr2-Jab1 complexes, demonstrating that Jab1-based inhibition of Brr2 presumably takes effect in all eukaryotes but is implemented via organism-specific molecular contacts. Moreover, the structures show that Brr2 auto-inhibition can act in concert with Jab1-mediated inhibition, and suggest that the N-terminal region influences how the Jab1 C-terminal tail interacts at the RNA-binding tunnel. Systematic RNA binding and unwinding studies revealed that the N-terminal region and the Jab1 C-terminal tail specifically interfere with accommodation of double-stranded and single-stranded regions of an RNA substrate, respectively, mutually reinforcing each other. Additionally, such analyses show that regulation based on the N-terminal region requires the presence of the inactive C-terminal helicase cassette. Together, our results outline an intricate system of regulatory mechanisms, which control Brr2 activities during snRNP assembly and splicing.
Keywords: Brr2; RNA helicase structure and function; X-ray crystallography; pre-mRNA splicing; remodeling of RNA-protein complexes; spliceosome catalytic activation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The large N-terminal region of the Brr2 RNA helicase guides productive spliceosome activation.Genes Dev. 2015 Dec 15;29(24):2576-87. doi: 10.1101/gad.271528.115. Epub 2015 Dec 4. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26637280 Free PMC article.
-
A noncanonical PWI domain in the N-terminal helicase-associated region of the spliceosomal Brr2 protein.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015 Apr;71(Pt 4):762-71. doi: 10.1107/S1399004715001005. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015. PMID: 25849387
-
Functions and regulation of the Brr2 RNA helicase during splicing.Cell Cycle. 2016 Dec 16;15(24):3362-3377. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1249549. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27792457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brr2 plays a role in spliceosomal activation in addition to U4/U6 unwinding.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Mar 31;43(6):3286-97. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv062. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25670679 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple genetic and biochemical interactions of Brr2, Prp8, Prp31, Prp1 and Prp4 kinase suggest a function in the control of the activation of spliceosomes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Curr Genet. 2005 Sep;48(3):151-61. doi: 10.1007/s00294-005-0013-6. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Curr Genet. 2005. PMID: 16133344 Review.
Cited by
-
Spliceosome assembly and regulation: insights from analysis of highly reduced spliceosomes.RNA. 2023 May;29(5):531-550. doi: 10.1261/rna.079273.122. Epub 2023 Feb 3. RNA. 2023. PMID: 36737103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA and Proteins: Mutual Respect.F1000Res. 2017 Mar 27;6:345. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.10572.1. eCollection 2017. F1000Res. 2017. PMID: 28408981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intrinsically disordered TSSC4 protein acts as a helicase inhibitor, placeholder and multi-interaction coordinator during snRNP assembly and recycling.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Mar 21;50(5):2938-2958. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac087. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35188580 Free PMC article.
-
An Allosteric Network for Spliceosome Activation Revealed by High-Throughput Suppressor Analysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2019 May;212(1):111-124. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.301922. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30898770 Free PMC article.
-
The inactive C-terminal cassette of the dual-cassette RNA helicase BRR2 both stimulates and inhibits the activity of the N-terminal helicase unit.J Biol Chem. 2020 Feb 14;295(7):2097-2112. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010964. Epub 2019 Dec 30. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31914407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wahl MC, Will CL, Lührmann R. The spliceosome: design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell 2009; 136:701-18; PMID:19239890; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Will CL, Lührmann R. Spliceosome structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011; 3:1-24; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a003707 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brow DA. Allosteric cascade of spliceosome activation. Annu Rev Genet 2002; 36:333-60; PMID:12429696; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.36.043002.091635 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Staley JP, Guthrie C. Mechanical devices of the spliceosome: motors, clocks, springs, and things. Cell 1998; 92:315-26; PMID:9476892; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80925-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Raghunathan PL, Guthrie C. RNA unwinding in U4/U6 snRNPs requires ATP hydrolysis and the DEIH-box splicing factor Brr2. Curr Biol 1998; 8:847-55; PMID:9705931; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0960-9822(07)00345-4 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
