Overexpressed Proteins in Hypervirulent Clade 8 and Clade 6 Strains of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Compared to E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 Clade 3 Strain
- PMID: 27880834
- PMCID: PMC5120812
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166883
Overexpressed Proteins in Hypervirulent Clade 8 and Clade 6 Strains of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Compared to E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 Clade 3 Strain
Abstract
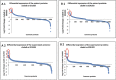
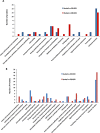
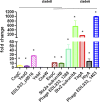
Escherichia coli O157:H7 is responsible for severe diarrhea and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), and predominantly affects children under 5 years. The major virulence traits are Shiga toxins, necessary to develop HUS and the Type III Secretion System (T3SS) through which bacteria translocate effector proteins directly into the host cell. By SNPs typing, E. coli O157:H7 was separated into nine different clades. Clade 8 and clade 6 strains were more frequently associated with severe disease and HUS. In this study, we aimed to identify differentially expressed proteins in two strains of E. coli O157:H7 (clade 8 and clade 6), obtained from cattle and compared them with the well characterized reference EDL933 strain (clade 3). Clade 8 and clade 6 strains show enhanced pathogenicity in a mouse model and virulence-related properties. Proteins were extracted and analyzed using the TMT-6plex labeling strategy associated with two dimensional liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry in tandem. We detected 2241 proteins in the cell extract and 1787 proteins in the culture supernatants. Attention was focused on the proteins related to virulence, overexpressed in clade 6 and 8 strains compared to EDL933 strain. The proteins relevant overexpressed in clade 8 strain were the curli protein CsgC, a transcriptional activator (PchE), phage proteins, Stx2, FlgM and FlgD, a dienelactone hydrolase, CheW and CheY, and the SPATE protease EspP. For clade 6 strain, a high overexpression of phage proteins was detected, mostly from Stx2 encoding phage, including Stx2, flagellin and the protease TagA, EDL933_p0016, dienelactone hydrolase, and Haemolysin A, amongst others with unknown function. Some of these proteins were analyzed by RT-qPCR to corroborate the proteomic data. Clade 6 and clade 8 strains showed enhanced transcription of 10 out of 12 genes compared to EDL933. These results may provide new insights in E. coli O157:H7 mechanisms of pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clade 8 and Clade 6 Strains of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from Cattle in Argentina have Hypervirulent-Like Phenotypes.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 1;10(6):e0127710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127710. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26030198 Free PMC article.
-
Coculture of Escherichia coli O157:H7 with a Nonpathogenic E. coli Strain Increases Toxin Production and Virulence in a Germfree Mouse Model.Infect Immun. 2015 Nov;83(11):4185-93. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00663-15. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26259815 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic features of human and bovine Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains isolated in Argentina.Int J Med Microbiol. 2016 Feb;306(2):123-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Int J Med Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26935026
-
Implication of virulence factors in Escherichia coil O157:H7 pathogenesis.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2003;29(4):277-96. doi: 10.1080/713608014. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14636040 Review.
-
A brief overview of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and its plasmid O157.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Jan;20(1):5-14. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20134227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the flanking region of the Shiga toxin operon in Stx2a bacteriophages reveals a diversity of the NanS-p sialate O-acetylesterase gene.AIMS Microbiol. 2023 Aug 2;9(3):570-590. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2023030. eCollection 2023. AIMS Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37649799 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of the virulence gene nleB among Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains.Heliyon. 2020 Jun 23;6(6):e04277. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04277. eCollection 2020 Jun. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32613131 Free PMC article.
-
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 antigens produced in transgenic lettuce effective as an oral vaccine in mice.Theor Appl Genet. 2023 Sep 23;136(10):214. doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04460-5. Theor Appl Genet. 2023. PMID: 37740735
-
Endocytosis, Cytotoxicity, and Translocation of Shiga Toxin-2 Are Stimulated by Infection of Human Intestinal (HCT-8) Monolayers With an Hypervirulent E. coli O157:H7 Lacking stx2 Gene.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Nov 21;9:396. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00396. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31824869 Free PMC article.
-
A Phenotypic Characterization of Two Isolates of a Multidrug-Resistant Outbreak Strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with Opposite Epidemiological Fitness.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Apr 8;2020:4741237. doi: 10.1155/2020/4741237. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32337252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rivas M, Padola NL, Lucchesi PMA, Massana M. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in Argentina In: Torres AG, editor. Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Latin America. Oak Park (IL), Estados Unidos: Bentham Science Publishers Ltd.; 2010. p. 142–61.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

