Anti-tumor effects of Abnormal Savda Munziq on the transplanted cervical cancer (U27) mouse model
- PMID: 27881109
- PMCID: PMC5122163
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1458-5
Anti-tumor effects of Abnormal Savda Munziq on the transplanted cervical cancer (U27) mouse model
Abstract
Background: Abnormal Savda Munziq (ASMq), a traditional uyghur medicine, has shown anti-tumour properties in vitro. it was showed that total flavonoids of ASMq could inhibit the proliferation and enhance the antioxidant ability of human cervix cancer HeLa cell. This study attempts to confirm these effects on the transplanted cervical cancer (U27) mouse model in vivo.
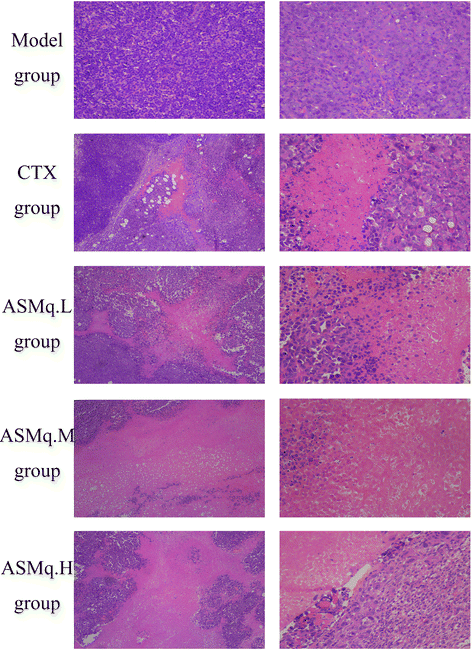
Methods: Forty eight Kunming mice were randomly divided in to six groups: normal control group (Control group), U27 tumor model group (Model group), cyclophosphamide administration group (CTX group),low-dose ASMq group (ASMq.L group), medium-dose ASMq group (ASMq.M group), and high-dose ASMq group (ASMq.H group). The five groups except normal control group transplanted with cervical cancer (U27) cells. We observed mice tumor inhibition rate and conducted the histopathological analysisUsing the western blot assay, the expression of TGF-β1 and TNF-α protein in transplanted cervical cancer U27 tumor tissue were detected.
Results: The tumor inhibition rates of CTX group, ASMq.L group, ASMq.M group, and ASMq.H group were 72.21, 31.27, 60.53 and 51.94% respectively, has obvious antitumor effect. ASMq significantly promote the spleen tlymphocyte proliferation of transplanted cervical cancer U27 mice. Invasive growth and diffusion rate in tumor tissue were accelerate in the transplanted cervical cancer U27 model group. Tumor tissue necrosis of tumor cells are smaller in the medium, high dosage group. Compared with the U27 model group, the expression levels of TGF-β1 protein and TNF-α protein expression exhibited statistically significant decreased in the mice tumor tissues in the CTX administration group and the ASMq administration group.
Conclusions: ASMq has some antitumor effects on U27 model mice in vivo, The effects are achieved not only by improving the immune function of U27 model mice, but also by inhibiting the expression levels of TGF-β1 protein while promoting the expression levels of TNF-α protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced efficacy with reduced toxicity of chemotherapy drug 5-fluorouracil by synergistic treatment with Abnormal Savda Munziq from Uyghur medicine.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Apr 7;17(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1685-4. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28388901 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced antitumor efficacy and reduced toxicity of Abnormal Savda Munziq on tumor bearing mice treated with chemotherapy.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 6;8(54):92682-92698. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21563. eCollection 2017 Nov 3. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29190948 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-carcinogenic effects of the phenolic-rich extract from abnormal Savda Munziq in association with its cytotoxicity, apoptosis-inducing properties and telomerase activity in human cervical cancer cells (SiHa).BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Feb 12;15:23. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0530-x. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 25880193 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary study of the effect of abnormal savda munziq on TGF-β1 and Smad7 expression in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jan 15;8(1):519-25. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25785025 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of traditional Uyghur medicine abnormal Savda Munziq extract on rabbit platelet aggregation in vitro and rat arteriovenous shunt thrombosis in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Jan 15;159:184-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.11.006. Epub 2014 Nov 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25449463
Cited by
-
ASMq protects against early burn wound progression in rats by alleviating oxidative stress and secondary mitochondria‑associated apoptosis via the Erk/p90RSK/Bad pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 May;23(5):390. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12029. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33760179 Free PMC article.
-
Bioassay-guided Isolation of Flavonoids from Caesalpinia bonduc (L.) Roxb. and Evaluation of Their Cytotoxicity.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Winter;20(1):274-282. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2020.112557.13824. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34400957 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic and Additive Effects of Herbal Medicines in Combination with Chemotherapeutics: A Scoping Review.Integr Cancer Ther. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15347354241259416. doi: 10.1177/15347354241259416. Integr Cancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 38867515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang G, He W, Cai M, Luo F, Kung H, Guan X, Zeng Y, Xie D. Loss/Down-regulation of tumor suppressor in lung cancer 1 expression is associated with tumor progression and is a biomarker of poor prognosis in ovarian carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011;21(3):486–93. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0b013e31820fa168. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Upur H, Dubrovin D, Amat N, Liu W, Moore N, Bauer R, et al. Greco-Arab-Uighur medicine. USA: Acupress; 2013.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical