Evaluation of efficacy and efficiency of a pragmatic intervention by a social worker to support informal caregivers of elderly patients (The ICE Study): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 27881145
- PMCID: PMC5122007
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1622-8
Evaluation of efficacy and efficiency of a pragmatic intervention by a social worker to support informal caregivers of elderly patients (The ICE Study): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Medical progress and the lifestyle modification have prolonged life expectancy, despite the development of chronic diseases. Support and care for older subjects are often provided by a network of informal caregivers composed of family, friends and neighbors, who are essential in helping older persons to continue living at home. It has been shown that the extent and diversity of informal tasks may jeopardize the physical, mental and social wellbeing of caregivers.
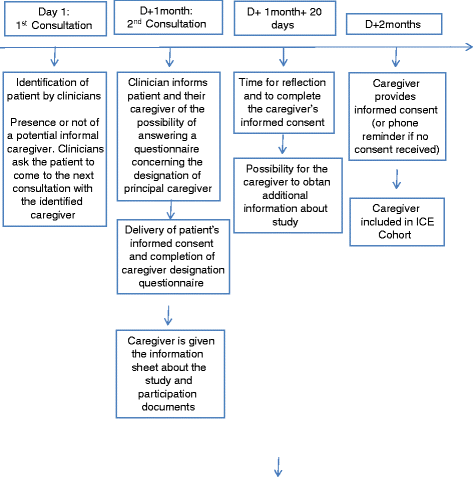
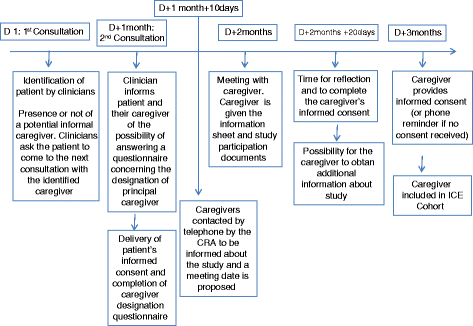
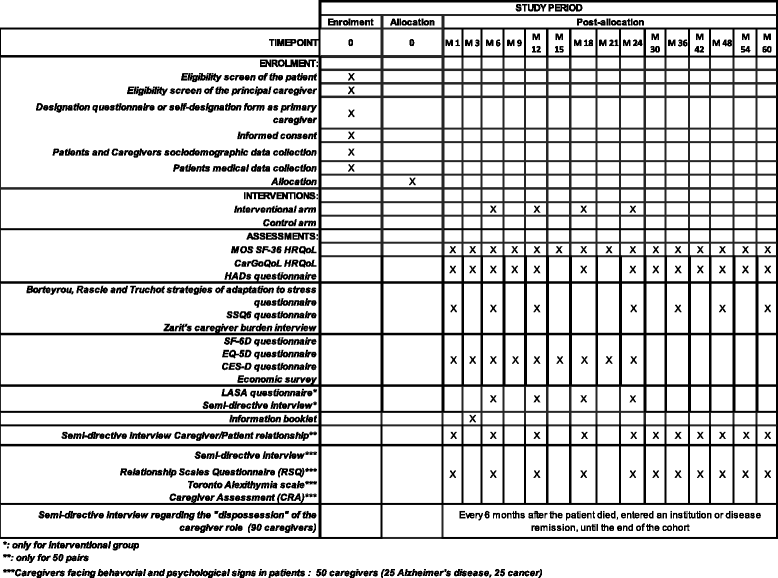
Methods/design: The aim of the Informal Carers of Elderly cohort is to define, through a longitudinal study, profiles of caregivers of older patients with a diagnosis of one of the following diseases: cancer (breast, prostate, colorectal), neurodegenerative diseases (Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and similar diseases), neurovascular diseases (stroke), sensory diseases (age-related macular degeneration (AMD)) and heart disease (heart failure). Patients must be at least 60 years old and living in the region of Burgundy-Franche-Comte (France). By following the different phases of the caregiving relationship from the announcement of the diagnosis, it will be possible to assess the quality of life of caregivers, coping strategies, levels of anxiety and depression, social support and the extent of their burden. We will also evaluate the efficacy and efficiency of the implementation of a pragmatic intervention by a social worker to help informal caregivers, through a randomized interventional trial nested in the cohort. Qualitative approaches aimed at studying the caregiver/patient relationship, and situations leading to breakdown of the caregiver relationship will be also undertaken.
Discussion: Through an analytical and longitudinal definition of profiles of informal caregivers, this study will gather detailed information on their life courses and their health trajectory by identifying consequences associated with the concept of their role as carers. In addition, the randomized interventional trial will explore the relevance of the implementation of a supportive intervention by a social worker to help caregivers. These data will help to identify strategies that could be used to improve the existing sources of aid and to propose new approaches to help caregivers. This study will provide the opportunity to identify the most relevant means of support adapted to caregivers, and provide an impulse for new health care policies.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02626377 . Retrospectively registered on 9 December 2015. Protocol date/version: 23 October 2014/version 2.
Keywords: Cancer; Chronic disease; Cost-utility; Elderly; Health-related quality of life; Informal caregivers; Longitudinal cohort study; Randomized study.
Figures
References
-
- Soullier N, Weber A. L’implication de l’entourage et des professionnels auprès des personnes âgées à domicile, DREES, Études et résultats, août 2011, n°771
-
- Fondation Novartis. Les aidants familiaux, Sondage BVA. Paris; 2010
-
- Goillot C, Mormiche P. Les enquêtes handicap incapacité et dépendance de 1998 et 1999, Insee Resultats, octobre 2003, n°22
-
- MACIF . Connaitre les aidants et leurs attentes. Paris: Sondage IFOP; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

