Primary Cilia and Mammalian Hedgehog Signaling
- PMID: 27881449
- PMCID: PMC5411695
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028175
Primary Cilia and Mammalian Hedgehog Signaling
Abstract
It has been a decade since it was discovered that primary cilia have an essential role in Hedgehog (Hh) signaling in mammals. This discovery came from screens in the mouse that identified a set of genes that are required for both normal Hh signaling and for the formation of primary cilia. Since then, dozens of mouse mutations have been identified that disrupt cilia in a variety of ways and have complex effects on Hedgehog signaling. Here, we summarize the genetic and developmental studies used to deduce how Hedgehog signal transduction is linked to cilia and the complex effects that perturbation of cilia structure can have on Hh signaling. We conclude by describing the current status of our understanding of the cell-type-specific regulation of ciliogenesis and how that determines the ability of cells to respond to Hedgehog ligands.
Copyright © 2017 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
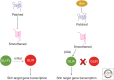
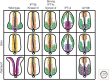
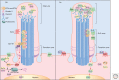

References
-
- Ahn S, Joyner AL. 2004. Dynamic changes in the response of cells to positive Hedgehog signaling during mouse limb patterning. Cell 118: 505–516. - PubMed
-
- Aughsteen AA. 2001. The ultrastructure of primary cilia in the endocrine and excretory duct cells of the pancreas of mice and rats. Eur J Morphol 39: 277–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
