Recurrent Hospitalization Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Undergoing Intracoronary Stenting Treated With 2 Treatment Strategies of Rivaroxaban or a Dose-Adjusted Oral Vitamin K Antagonist Treatment Strategy
- PMID: 27881555
- PMCID: PMC5266420
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.025783
Recurrent Hospitalization Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Undergoing Intracoronary Stenting Treated With 2 Treatment Strategies of Rivaroxaban or a Dose-Adjusted Oral Vitamin K Antagonist Treatment Strategy
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Recurrent Hospitalization Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Undergoing Intracoronary Stenting Treated With 2 Treatment Strategies of Rivaroxaban or a Dose-Adjusted Oral Vitamin K Antagonist Treatment Strategy.Circulation. 2017 Mar 21;135(12):e789. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000495. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28320814 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Patients with atrial fibrillation who undergo intracoronary stenting traditionally are treated with a vitamin K antagonist (VKA) plus dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT), yet this treatment leads to high risks of bleeding. We hypothesized that a regimen of rivaroxaban plus a P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy or rivaroxaban plus DAPT could reduce bleeding and thereby have a favorable impact on all-cause mortality and the need for rehospitalization.
Methods: Stented subjects with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (n=2124) were randomized 1:1:1 to administration of reduced-dose rivaroxaban 15 mg daily plus a P2Y12 inhibitor for 12 months (group 1); rivaroxaban 2.5 mg twice daily with stratification to a prespecified duration of DAPT of 1, 6, or 12 months (group 2); or the reference arm of dose-adjusted VKA daily with a similar DAPT stratification (group 3). The present post hoc analysis assessed the end point of all-cause mortality or recurrent hospitalization for an adverse event, which was further classified as the result of bleeding, a cardiovascular cause, or another cause blinded to treatment assignment.
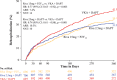
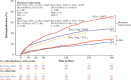
Results: The risk of all-cause mortality or recurrent hospitalization was 34.9% in group 1 (hazard ratio=0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.66-0.94; P=0.008 versus group 3; number needed to treat=15), 31.9% in group 2 (hazard ratio=0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.62-0.90; P=0.002 versus group 3; number needed to treat=10), and 41.9% in group 3 (VKA+DAPT). Both all-cause death plus hospitalization potentially resulting from bleeding (group 1=8.6% [P=0.032 versus group 3], group 2=8.0% [P=0.012 versus group 3], and group 3=12.4%) and all-cause death plus rehospitalization potentially resulting from a cardiovascular cause (group 1=21.4% [P=0.001 versus group 3], group 2=21.7% [P=0.011 versus group 3], and group 3=29.3%) were reduced in the rivaroxaban arms compared with the VKA arm, but other forms of rehospitalization were not.
Conclusions: Among patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing intracoronary stenting, administration of either rivaroxaban 15 mg daily plus P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy or 2.5 mg rivaroxaban twice daily plus DAPT was associated with a reduced risk of all-cause mortality or recurrent hospitalization for adverse events compared with standard-of-care VKA plus DAPT.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT01830543.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; percutaneous coronary intervention; rivaroxaban; vitamin K.
© 2016 The Authors.
Figures


Comment in
-
O PIONEERs! The Beginning of the End of Full-Dose Triple Therapy with Warfarin?Circulation. 2017 Jan 24;135(4):334-337. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.025923. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 27881554 No abstract available.
-
Atrial fibrillation: A safe alternative to warfarin plus DAPT after PCI?Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017 Jan;14(1):4-5. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.201. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27905477 No abstract available.
-
Letter by Cerit Regarding Article, "Recurrent Hospitalization Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Undergoing Intracoronary Stenting Treated With 2 Treatment Strategies of Rivaroxaban or a Dose-Adjusted Oral Vitamin K Antagonist Treatment Strategy".Circulation. 2017 Jul 4;136(1):115-116. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027683. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28674097 No abstract available.
-
Response by Gibson and Fox to Letter Regarding Article, "Recurrent Hospitalization Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Undergoing Intracoronary Stenting Treated With 2 Treatment Strategies of Rivaroxaban or a Dose-Adjusted Oral Vitamin K Antagonist Treatment Strategy".Circulation. 2017 Jul 4;136(1):117. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028416. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28674098 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rubboli A, Colletta M, Herzfeld J, Sangiorgio P, Di Pasquale G. Periprocedural and medium-term antithrombotic strategies in patients with an indication for long-term anticoagulation undergoing coronary angiography and intervention. Coron Artery Dis. 2007;18:193–199. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0b013e328012a964. - PubMed
-
- Wang TY, Robinson LA, Ou F-S, Roe MT, Ohman EM, Gibler WB, Smith SC, Peterson ED, Becker RC. Discharge antithrombotic strategies among patients with acute coronary syndrome previously on warfarin anticoagulation: physician practice in the CRUSADE registry. Am Heart J. 2008;155:361–368. - PubMed
-
- Pérez-Gómez F, Alegría E, Berjón J, Iriarte JA, Zumalde J, Salvador A, Mataix L NASPEAF Investigators. Comparative effects of antiplatelet, anticoagulant, or combined therapy in patients with valvular and nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: a randomized multicenter study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:1557–1566. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.05.084. - PubMed
-
- Leon MB, Baim DS, Popma JJ, Gordon PC, Cutlip DE, Ho KK, Giambartolomei A, Diver DJ, Lasorda DM, Williams DO, Pocock SJ, Kuntz RE. A clinical trial comparing three antithrombotic-drug regimens after coronary-artery stenting: Stent Anticoagulation Restenosis Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1665–1671. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199812033392303. - PubMed
-
- Connolly S, Pogue J, Hart R, Pfeffer M, Hohnloser S, Chrolavicius S, Pfeffer M, Hohnloser S, Yusuf S. Clopidogrel plus aspirin versus oral anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation in the Atrial fibrillation Clopidogrel Trial with Irbesartan for prevention of Vascular Events (ACTIVE W): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2006;367:1903–1912. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

