Bicarbonate Balance and Prescription in ESRD
- PMID: 27881607
- PMCID: PMC5328170
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2016070780
Bicarbonate Balance and Prescription in ESRD
Abstract
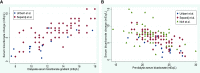
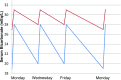
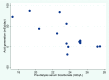
The optimal approach to managing acid-base balance is less well defined for patients receiving hemodialysis than for those receiving peritoneal dialysis. Interventional studies in hemodialysis have been limited and inconsistent in their findings, whereas more compelling data are available from interventional studies in peritoneal dialysis. Both high and low serum bicarbonate levels associate with an increased risk of mortality in patients receiving hemodialysis, but high values are a marker for poor nutrition and comorbidity and are often highly variable from month to month. Measurement of pH would likely provide useful additional data. Concern has arisen regarding high-bicarbonate dialysate and dialysis-induced alkalemia, but whether these truly cause harm remains to be determined. The available evidence is insufficient for determining the optimal target for therapy at this time.
Keywords: acidosis; dialysis; electrolytes.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Lyon DM, Dunlop DM, Stewart CP: The alkaline treatment of chronic nephritis. Lancet 218: 1009–1013, 1931
-
- Kolff WJ: Artificial kidney; treatment of acute and chronic uremia. Cleve Clin Q 17: 216–228, 1950 - PubMed
-
- Sanchezsicilia L, Kolff WJ: Acid-base equilibrium in patients with chronic renal failure in whom life is sustained by periodic hemodialyses. Report of five representative cases. Cleve Clin Q 31: 127–139, 1964 - PubMed
-
- Safety Alerts for Human Medical Products - Dialysate Concentrates Used in Hemodialysis: Safety communication - alkali dosing errors. Available at http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHuma.... Accessed November14, 2012
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

