Lowered H3K27me3 and DNA hypomethylation define poorly prognostic pediatric posterior fossa ependymomas
- PMID: 27881822
- PMCID: PMC5123566
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aah6904
Lowered H3K27me3 and DNA hypomethylation define poorly prognostic pediatric posterior fossa ependymomas
Abstract
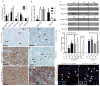
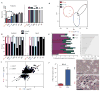
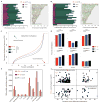
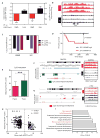
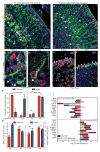
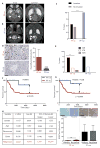
Childhood posterior fossa (PF) ependymomas cause substantial morbidity and mortality. These tumors lack recurrent genetic mutations, but a subset of these ependymomas exhibits CpG island (CpGi) hypermethylation [PF group A (PFA)], implicating epigenetic alterations in their pathogenesis. Further, histological grade does not reliably predict prognosis, highlighting the importance of developing more robust prognostic markers. We discovered global H3K27me3 reduction in a subset of these tumors (PF-ve ependymomas) analogous to H3K27M mutant gliomas. PF-ve tumors exhibited many clinical and biological similarities with PFA ependymomas. Genomic H3K27me3 distribution showed an inverse relationship with CpGi methylation, suggesting that CpGi hypermethylation drives low H3K27me3 in PF-ve ependymomas. Despite CpGi hypermethylation and global H3K27me3 reduction, these tumors showed DNA hypomethylation in the rest of the genome and exhibited increased H3K27me3 genomic enrichment at limited genomic loci similar to H3K27M mutant gliomas. Combined integrative analysis of PF-ve ependymomas with H3K27M gliomas uncovered common epigenetic deregulation of select factors that control radial glial biology, and PF radial glia in early human development exhibited reduced H3K27me3. Finally, H3K27me3 immunostaining served as a biomarker of poor prognosis and delineated radiologically invasive tumors, suggesting that reduced H3K27me3 may be a prognostic indicator in PF ependymomas.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
C.B.T is co-founder of Agios Pharmaceuticals and has financial interest in Agios. C.B.T is also on the Board of Directors of Merck and CRL. The authors of this study declare no other potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Reduced H3K27me3 is a New Epigenetic Biomarker for Pediatric Posterior Fossa Ependymomas.Neurosurgery. 2017 Jul 1;81(1):N7-N8. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyx262. Neurosurgery. 2017. PMID: 28873995 No abstract available.
References
-
- Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Kleihues P, Ellison DW. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. - PubMed
-
- Pajtler KW, Witt H, Sill M, Jones DT, Hovestadt V, Kratochwil F, Wani K, Tatevossian R, Punchihewa C, Johann P, Reimand J, Warnatz HJ, Ryzhova M, Mack S, Ramaswamy V, Capper D, Schweizer L, Sieber L, Wittmann A, Huang Z, van Sluis P, Volckmann R, Koster J, Versteeg R, Fults D, Toledano H, Avigad S, Hoffman LM, Donson AM, Foreman N, Hewer E, Zitterbart K, Gilbert M, Armstrong TS, Gupta N, Allen JC, Karajannis MA, Zagzag D, Hasselblatt M, Kulozik AE, Witt O, Collins VP, von Hoff K, Rutkowski S, Pietsch T, Bader G, Yaspo ML, von Deimling A, Lichter P, Taylor MD, Gilbertson R, Ellison DW, Aldape K, Korshunov A, Kool M, Pfister SM. Molecular Classification of Ependymal Tumors across All CNS Compartments, Histopathological Grades, and Age Groups. Cancer cell. 2015;27:728–743. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grundy RG, Wilne SA, Weston CL, Robinson K, Lashford LS, Ironside J, Cox T, Chong WK, Campbell RH, Bailey CC, Gattamaneni R, Picton S, Thorpe N, Mallucci C, English MW, Punt JA, Walker DA, Ellison DW, Machin D C Children’s. C. Leukaemia Group Brain Tumour. Primary postoperative chemotherapy without radiotherapy for intracranial ependymoma in children: the UKCCSG/SIOP prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:696–705. - PubMed
-
- Merchant TE, Mulhern RK, Krasin MJ, Kun LE, Williams T, Li C, Xiong X, Khan RB, Lustig RH, Boop FA, Sanford RA. Preliminary results from a phase II trial of conformal radiation therapy and evaluation of radiation-related CNS effects for pediatric patients with localized ependymoma. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2004;22:3156–3162. - PubMed
-
- Parker M, Mohankumar KM, Punchihewa C, Weinlich R, Dalton JD, Li Y, Lee R, Tatevossian RG, Phoenix TN, Thiruvenkatam R, White E, Tang B, Orisme W, Gupta K, Rusch M, Chen X, Li Y, Nagahawhatte P, Hedlund E, Finkelstein D, Wu G, Shurtleff S, Easton J, Boggs K, Yergeau D, Vadodaria B, Mulder HL, Becksfort J, Gupta P, Huether R, Ma J, Song G, Gajjar A, Merchant T, Boop F, Smith AA, Ding L, Lu C, Ochoa K, Zhao D, Fulton RS, Fulton LL, Mardis ER, Wilson RK, Downing JR, Green DR, Zhang J, Ellison DW, Gilbertson RJ. C11orf95-RELA fusions drive oncogenic NF-kappaB signalling in ependymoma. Nature. 2014;506:451–455. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

