Exercise training attenuates renovascular hypertension partly via RAS- ROS- glutamate pathway in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus
- PMID: 27881877
- PMCID: PMC5121597
- DOI: 10.1038/srep37467
Exercise training attenuates renovascular hypertension partly via RAS- ROS- glutamate pathway in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus
Abstract
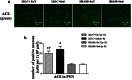
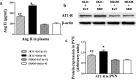
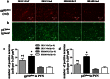
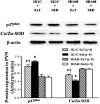
Exercise training (ExT) has been reported to benefit hypertension; however, the exact mechanisms involved are unclear. We hypothesized that ExT attenuates hypertension, in part, through the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and glutamate in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN). Two-kidney, one-clip (2K1C) renovascular hypertensive rats were assigned to sedentary (Sed) or treadmill running groups for eight weeks. Dizocilpine (MK801), a glutamate receptor blocker, or losartan (Los), an angiotensin II type1 receptor (AT1-R) blocker, were microinjected into the PVN at the end of the experiment. We found that 2K1C rats had higher mean arterial pressure (MAP) and renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA). These rats also had excessive oxidative stress and overactivated RAS in PVN. Eight weeks of ExT significantly decreased MAP and RSNA in 2K1C hypertensive rats. ExT inhibited angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), AT1-R, and glutamate in the PVN, and angiotensin II (ANG II) in the plasma. Moreover, ExT attenuated ROS by augmenting copper/zinc superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD) and decreasing p47phox and gp91phox in the PVN. MK801or Los significantly decreased blood pressure in rats. Together, these findings suggest that the beneficial effects of ExT on renovascular hypertension may be, in part, through the RAS-ROS-glutamate pathway in the PVN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chronic infusion of lisinopril into hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus modulates cytokines and attenuates oxidative stress in rostral ventrolateral medulla in hypertension.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Sep 1;279(2):141-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.06.004. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24937322
-
Chronic infusion of enalaprilat into hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates angiotensin II-induced hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy by restoring neurotransmitters and cytokines.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Feb 1;274(3):436-44. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24342267
-
Inhibition of reactive oxygen species in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates the renin-angiotensin system and proinflammatory cytokines in hypertension.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Apr 15;276(2):115-20. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.02.002. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24576725
-
Mechanisms of renal sympathetic activation in renovascular hypertension.Exp Physiol. 2015 Apr 20;100(5):496-501. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2014.079855. Exp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25639235 Review.
-
Losartan chemistry and its effects via AT1 mechanisms in the kidney.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(28):3701-15. doi: 10.2174/092986709789105000. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19747145 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exercise Training Attenuates Hypertension via Suppressing ROS/MAPK/NF-κB/AT-1R Pathway in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 24;14(19):3968. doi: 10.3390/nu14193968. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235619 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolites and Hypertension: Insights into Hypertension as a Metabolic Disorder: 2019 Harriet Dustan Award.Hypertension. 2020 Jun;75(6):1386-1396. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.13896. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32336227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intermedin in Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates Ang II-Induced Sympathoexcitation through the Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase-Dependent ROS Generation in Obese Rats with Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 28;20(17):4217. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174217. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31466304 Free PMC article.
-
Evans Blue Reduces Neuropathic Pain Behavior by Inhibiting Spinal ATP Release.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 9;20(18):4443. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184443. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31505901 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise protects vascular function by countering senescent cells in older adults.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 6;14:1138162. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1138162. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37089434 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Laterza M. C. et al.. Exercise training restores baroreflex sensitivity in never-treated hypertensive patients. Hypertension 49, 1298–1306 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Gao L. et al.. Exercise training normalizes sympathetic outflow by central antioxidant mechanisms in rabbits with pacing-induced chronic heart failure. Circulation 115, 3095–3102 (2007). - PubMed
-
- de Abreu S. B. et al.. Role of paraventricular nucleus in exercise training-induced autonomic modulation in conscious rats. Auton Neurosci 148, 28–35 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Zheng H. et al.. Exercise training improves endogenous nitric oxide mechanisms within the paraventricular nucleus in rats with heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288, H2332–H234 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Higa-Taniguchi K. T. et al.. Exercise training-induced remodeling of paraventricular nucleus (nor) adrenergic innervation in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292, R1717–R1727 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

