Effects of Ramipril and Telmisartan on Plasma Concentrations of Low Molecular Weight and Protein Thiols and Carotid Intima Media Thickness in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 27881888
- PMCID: PMC5110866
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/1821596
Effects of Ramipril and Telmisartan on Plasma Concentrations of Low Molecular Weight and Protein Thiols and Carotid Intima Media Thickness in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
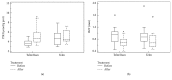
Hypertension, a common feature in chronic kidney disease (CKD), is an independent risk factor for CKD progression and cardiovascular disease. Although inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) exert salutary effects on blood pressure control and proteinuria in CKD patients, their activity towards traditional and novel oxidative markers is largely unknown. We studied the effects of 6-month treatment with telmisartan versus a combination of telmisartan and ramipril on plasma concentrations of low molecular mass (LMW, including homocysteine and cysteine) and protein thiols (PSH) plasma concentration and their relationships with carotid intima media thickness (IMT), in 24 hypertensive CKD patients (age 60 ± 12 years, 8 females and 16 males). Pretreatment PSH concentrations were independently associated with IMT (r = -0.42, p = 0.039). Neither treatment affected plasma LMW thiols, in both reduced and total form. By contrast, both treatments increased PSH plasma concentrations and reduced IMT, although significant differences were only observed in the combined treatment group. Our results suggest that the beneficial effects of combined RAS inhibitor treatment on IMT in hypertensive CKD patients may be mediated by a reduction of oxidative stress markers, particularly PSH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ventricular and vascular remodelling effects of the angiotensin II receptor blocker telmisartan and/or the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor ramipril in hypertensive patients.J Int Med Res. 2005;33 Suppl 1:39A-49A. doi: 10.1177/14732300050330S106. J Int Med Res. 2005. PMID: 16222899 Clinical Trial.
-
Combination therapy with renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitor telmisartan and serine protease inhibitor camostat mesilate provides further renoprotection in a rat chronic kidney disease model.J Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Feb;130(2):110-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Jan 20. J Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26887332
-
Evaluation of fixed dose combination (FDC) of telmisartan+ramipril usage in patients with micro-albuminuria and persistent hypertension: A TRIUMPH study.J Indian Med Assoc. 2008 Mar;106(3):191-4, 196. J Indian Med Assoc. 2008. PMID: 18712142 Clinical Trial.
-
Telmisartan in high-risk cardiovascular patients.Am J Cardiol. 2010 Jan 4;105(1 Suppl):36A-43A. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.10.008. Am J Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20102972 Review.
-
Telmisartan: just an antihypertensive agent? A literature review.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011 Dec;12(17):2719-35. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2011.632367. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011. PMID: 22077832 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous Risk Factor Control Using Telehealth to slOw Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease (STOP-DKD) study: Protocol and baseline characteristics of a randomized controlled trial.Contemp Clin Trials. 2018 Jun;69:28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Contemp Clin Trials. 2018. PMID: 29649631 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Blood Pressure Control on Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2025 Jun 17;17(6):e86230. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86230. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40677434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular Risk Assessment Using Ultrasonographic Surrogate Markers of Atherosclerosis and Arterial Stiffness in Patients With Chronic Renal Impairment: A Narrative Review of the Evidence and a Critical View of Their Utility in Clinical Practice.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2020 Sep 10;7:2054358120954939. doi: 10.1177/2054358120954939. eCollection 2020. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32963791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood Thiol Redox State in Chronic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 5;23(5):2853. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052853. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Szarejko-Paradowska A., Gluba-Brzózka A., Pietruszyński R., Rysz J. Assessment of the relationship between selected cardiovascular risk factors and the indices of intima-media thickness and coronary artery calcium score in various stages of chronic kidney disease. International Urology and Nephrology. 2015;47(12):2003–2012. doi: 10.1007/s11255-015-1132-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical