Genetic and immunohistochemical analysis of HSPA5 in mouse and human retinas
- PMID: 27881906
- PMCID: PMC5108462
Genetic and immunohistochemical analysis of HSPA5 in mouse and human retinas
Abstract
Purpose: Photoreceptor degenerative diseases are among the leading causes of vision loss. Although the causative genetic mutations are often known, mechanisms leading to photoreceptor degeneration remain poorly defined. We have previously demonstrated that the photoreceptor membrane-associated protein XAP-1 antigen is a product of the HSPA5 gene. In this study, we used systems genetic methods, statistical modeling, and immunostaining to identify and analyze candidate genes that modulate Hspa5 expression in the retina.
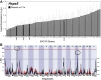
Methods: Quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping was used to map the genomic region that regulates Hspa5 in the cross between C57BL/6J X DBA/2J mice (BXD) genetic reference panel. The stepwise refinement of candidate genes was based on expression QTL mapping, gene expression correlation analyses (direct and partial), and analysis of regional sequence variants. The subcellular localization of candidate proteins and HSPA5 in mouse and human retinas was evaluated by immunohistochemistry. Differences in the localization of extracellular HSPA5 were assessed between healthy human donor and atrophic age-related macular degeneration (AMD) donor eyes.
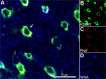
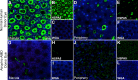
Results: In the eyes of healthy mice, extracellular HSPA5 was confined to the area around the cone photoreceptor outer segments. Mapping variation in Hspa5 mRNA expression levels in the retina revealed a statistically significant trans-acting expression QTL (eQTL) on Chromosome 2 (Chr 2) and a suggestive locus on Chr 15. Sulf2 on Chr 2 was the strongest candidate gene based on partial correlation analysis, Pearson correlation with Hspa5, expression levels in the retina, a missense variant in exon 14, and its reported function in the extracellular matrix and interphotoreceptor matrix. SULF2 is localized to the rod and cone photoreceptors in both human and mouse retinas. In human retinas with no pathology, extracellular HSPA5 was localized around many cones within the macular area. In contrast, fewer HSPA5-immunopositive cones were observed in the retinas from AMD donors.
Conclusions: We identified Sulf2 as a candidate gene modulating the Hspa5 expression in the retina. The preferential loss of HSPA5 in the interphotoreceptor matrix around cone photoreceptors in atrophic AMD retinas opens up new avenues for exploring the changes in interphotoreceptor matrix (IPM) that are associated with macular disease.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Deletion of the Impg2 gene causes the degeneration of rod and cone cells in mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Jun 27;29(10):1624-1634. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa062. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32242237
-
Redistribution of insoluble interphotoreceptor matrix components during photoreceptor differentiation in the mouse retina.J Comp Neurol. 1994 Jul 1;345(1):115-24. doi: 10.1002/cne.903450109. J Comp Neurol. 1994. PMID: 8089273
-
Growth of the postnatal rat retina in vitro: quantitative RT-PCR analyses of mRNA expression for photoreceptor proteins.Mol Vis. 2003 Dec 9;9:657-64. Mol Vis. 2003. PMID: 14685147
-
[Molecular cell glycobiology of the retina].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1993 Dec;97(12):1370-93. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1993. PMID: 8291480 Review. Japanese.
-
Defective cone photoreceptor cytoskeleton, alignment, feedback, and energetics can lead to energy depletion in macular degeneration.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004 Sep;23(5):495-522. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2004.04.005. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004. PMID: 15302348 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-genomic behavioral genetics: From revolution to routine.Genes Brain Behav. 2018 Mar;17(3):e12441. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12441. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Genes Brain Behav. 2018. PMID: 29193773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD, Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM, Green DR. Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:469–75. - PubMed
-
- Delpino A, Castelli M. The 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78/BIP) is expressed on the cell membrane, is released into cell culture medium and is also present in human peripheral circulation. Biosci Rep. 2002;22:407–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

